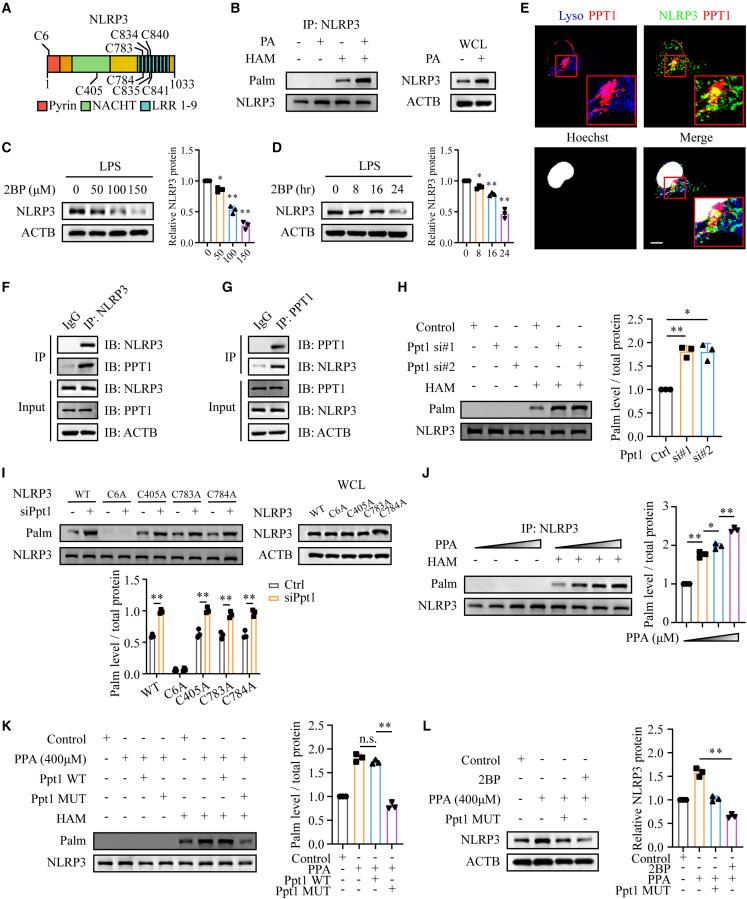
Figure 5.
Phenylpyruvate upregulated NLRP3 palmitoylation by binding to the PPT1 protein
(A) Schematic view of NLRP3 (full length) and the location of the S-palmitoylation sites.
(B) ABE assay and immunoblot analysis were used to evaluate NLRP3 palmitoylation in BMDMs treated with or without palmitic acid (n = 3).
(C) Immunoblot and statistical analysis showing NLRP3 expression in BMDMs treated with 2BP at the indicated concentrations (0, 50, 100, and 150 μM) for 24 h (n = 3).
(D) Immunoblot and statistical analysis showing NLRP3 expression in BMDMs treated with 2BP (100 μM) for 0, 8, 16, and 24 h (n = 3).
(E) Immunostaining of the location of LAMP2 (indicating lysosomes), PPT1, and NLRP3 in macrophages. The nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(F and G) Immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblot analysis were used to detect the endogenous NLRP3 and PPT1 association in macrophages (n = 3).
(H) ABE assay and immunoblot analysis were used to evaluate NLRP3 palmitoylation in BMDMs with Ppt1 knockdown (n = 3).
(I) Mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) were transfected with WT NLRP3 or the indicated NLRP3 mutants for 24 h with or without knockdown of Ppt1. ABE assay and immunoblot analysis showing palmitoylation levels of the indicated NLRP3 mutants (n = 3).
(J) ABE assay and immunoblot analysis were used to determine NLRP3 palmitoylation levels in BMDMs treated with increasing phenylpyruvate concentrations (n = 3).
(K) Determination of NLRP3 palmitoylation levels in BMDMs treated with 400 μM phenylpyruvate and then transfected with the Ppt1 WT plasmid or the MUT plasmid for 24 h (n = 3).
(L) BMDMs were treated with 400 μM phenylpyruvate with or without 100 μM 2BP and then transfected with or without the Ppt1 MUT plasmid. ABE assay and immunoblot analysis determining NLRP3 palmitoylation levels in the indicated cells (n = 3). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant.