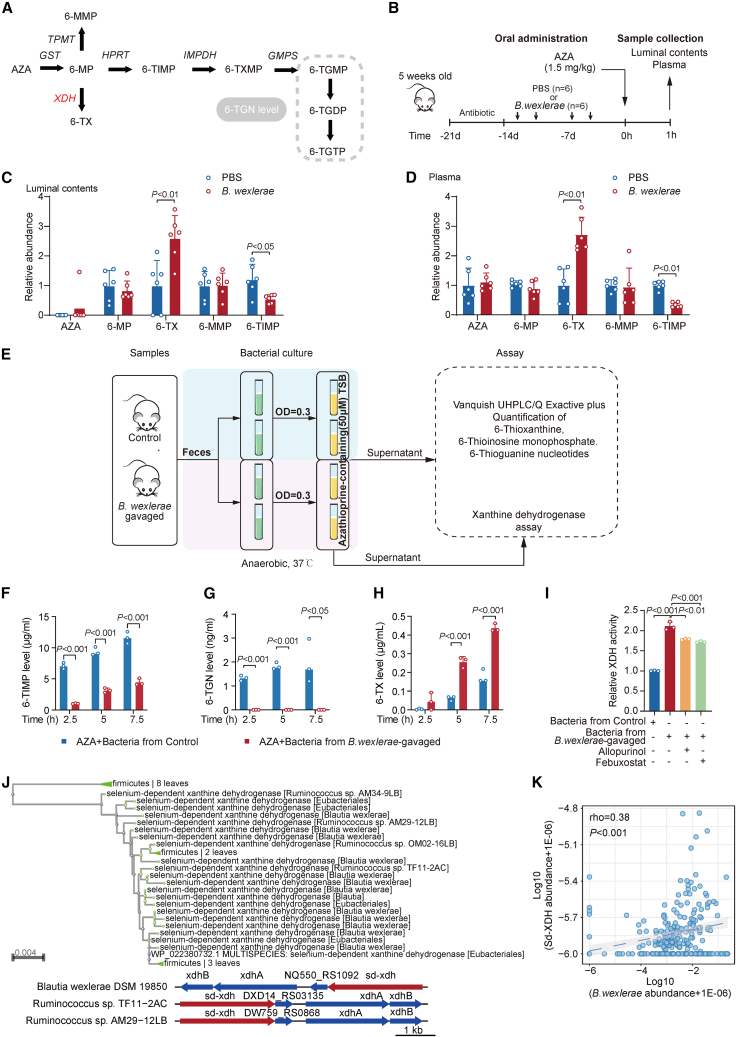
Figure 5.
B. wexlerae was closely associated with the biotransformation of AZA
(A) Proposed thiopurine metabolism. AZA, azathioprine; 6-MP, 6-mercaptopurine; 6-TIMP, 6-thioinosine monophosphate; 6-TXMP, 6-thioxanthosine monophosphate; 6-TGMP, 6-thioguanine monophosphate; 6-TGDP, 6-thioguanine diphosphate; 6-TGTP, 6-thioguanine triphosphate; 6-TGN, 6-thioguanine; GST, glutathione S-transferase; HPRT, hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase; IMPDH, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; GMPS, guanosine monophosphate synthetase. In therapeutic drug monitoring, a 6-TGN level consists of the sum of 6-TGMP, 6-TGDP, and 6-TGTP levels.
(B) Schematic overview of experimental design for studying the effect of B. wexlerae and B. luti on AZA bioavailability in C57BL/6 mice. n = 6 for each group.
(C and D) Quantitative analysis of AZA and its metabolite levels in luminal contents (C) and plasma (D). n = 6/group, non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(E) Schematic overview of experimental design for studying the impact of B. wexlerae on AZA in vitro. The green tube contains fecal bacterial suspension (OD = 0.3). The yellow tube contains fecal bacterial suspension (OD = 0.3) with AZA supplement. Control mice (blue block). B. wexlerae-gavaged mice (purple block).
(F–H) Quantitative levels of 6-TIMP (F), 6-TGN (G), and 6-TX (H) in AZA-containing culture medium post-anaerobic incubation with fecal samples. n = 3/group, Student’s t test. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(I) XDH activity in the medium exposed to fecal samples under anaerobic conditions. n = 3/group, Student’s T test. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(J) Bioinformatic analysis showing B. wexlere might encode a selenium-dependent xanthine dehydrogenase (sd-XDH) gene.
(K) Correlation analysis of bacterial sd-XDH and B. wexlerae in PRJNA385949.