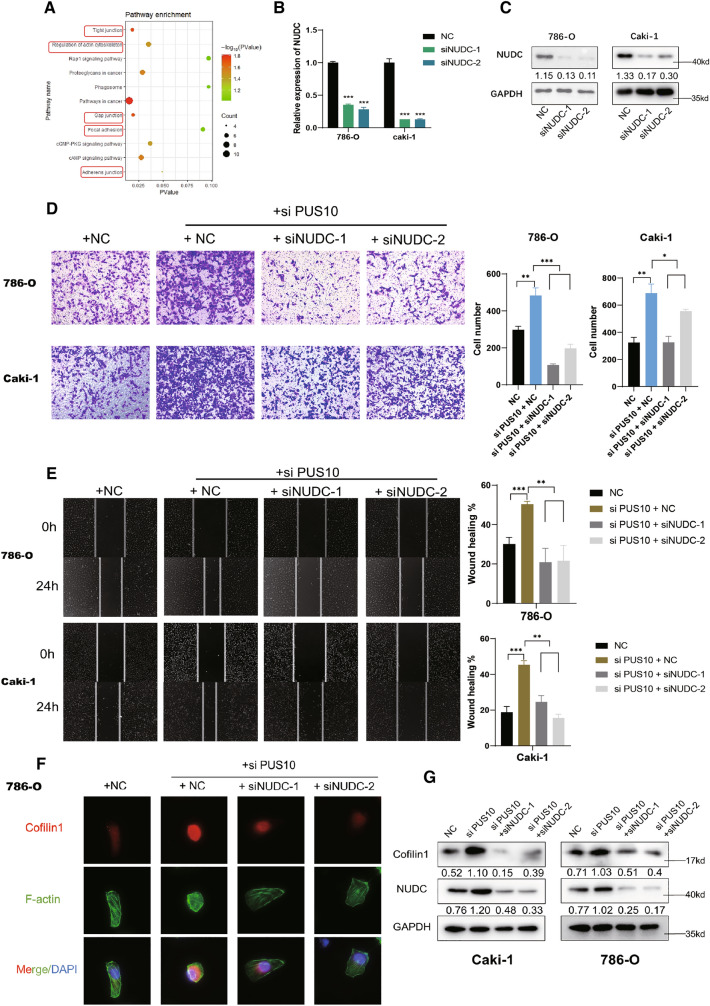
Fig. 6.
The NUDC/cofilin1-dependent cytoskeleton is involved in the PUS10-induced migration suppression of RCC. A KEGG enrichment analysis of the genes possessing a negative correlation with PUS10 in KIRC. B, C The efficiency of NUDC silencing was demonstrated at the mRNA and protein levels. D Transwell assays revealed that NUDC depletion abrogated the promoted migration caused by PUS10 knockdown in Caki-1 and 786-O cells. Migrating cells in three replicate experiments were counted and are presented as the mean ± SD in the histogram. E Wound healing assays showed that NUDC depletion reversed the enhanced wound healing rate induced by PUS10 knockdown in Caki-1 and 786-O cells. Three replicate experiments were conducted, and the results are presented as the mean ± SD in the histogram. F Representative images of immunostaining using anti-cofilin1 antibody and phalloidin are shown, showing the impact of PUS10 on the cofilin1-dependent cytoskeleton. G Western blot assays showed that the increased expression of Coflin1 induced by PUS10 knockdown was rescued by NUDC depletion in Caki-1 and 786-O cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns not significant