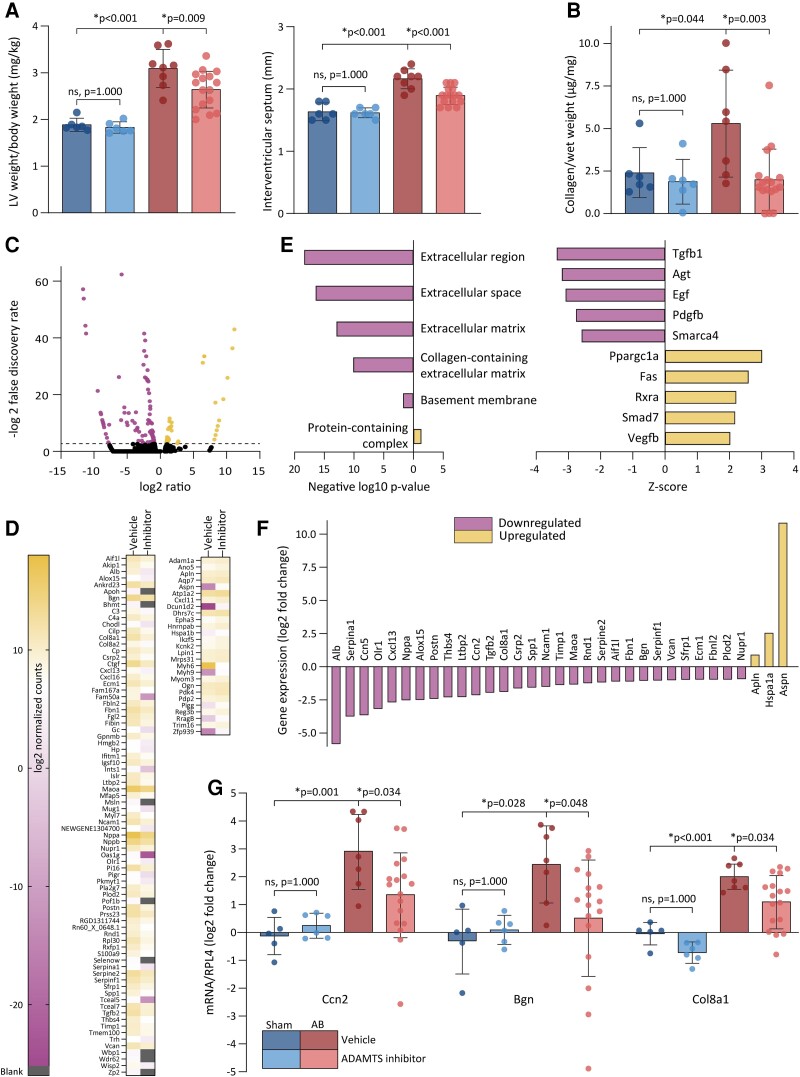
Figure 2.
Effects of ADAMTS inhibition on remodelling and disease pathways. (A) LV weight to body weight measured at necropsy (left) and interventricular wall thickness measured by echocardiography (right) 8 weeks after AB or sham surgery (sham vehicle n = 6, sham ADAMTS inhibitor n = 6, AB vehicle n = 8, AB ADAMTS inhibitor n = 17). (B) Fibrosis in LV as determined by the total collagen content as a proportion of wet weight quantified by HPLC. (C) Volcano plot showing the expression of genes with a false discovery rate less than 0.15 (black dots), up-regulated (yellow dots), and down-regulated genes (purple dots). Dotted line indicates a false discovery rate of 0.15. (D) Heatmap showing log2-transformed normalized counts of DEGs that were down-regulated (left) and up-regulated (right) in AB rats treated with vehicle and ADAMTS inhibitor. Genes with LOC and AARB prefixes are omitted. (E) Enrichment of DEGs in cellular compartments assessed by overrepresentation test of genes that were down-regulated (purple) or up-regulated (yellow) in AB rats treated with ADAMTS inhibitor compared with those treated with vehicle (left). Upstream regulators identified in IPA ranked by their Z-score (right). (F) Gene expression of DEGs that are identified as TGF-β target genes by IPA. (G) mRNA expression of selected TGF-β-inducible genes in myocardial samples determined by RT–qPCR (sham vehicle n = 5, sham ADAMTS inhibitor n = 6, AB vehicle n = 7, AB ADAMTS inhibitor n = 17). Bars represent mean ± 1 SD. Groups were compared by one-way ANOVA with planned comparisons followed by Bonferroni correction for the following comparisons: sham vehicle vs. sham ADAMTS4 inhibitor, sham vehicle vs. AB vehicle, and AB vehicle vs. AB ADAMTS inhibitor. P < 0.05 were considered significant and marked with *. LV, left ventricle; AB, aortic banding; ADAMTS4, a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin motif; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; TGF, transforming growth factor; HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography; IPA, Ingenuity pathways analysis; RT–qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.