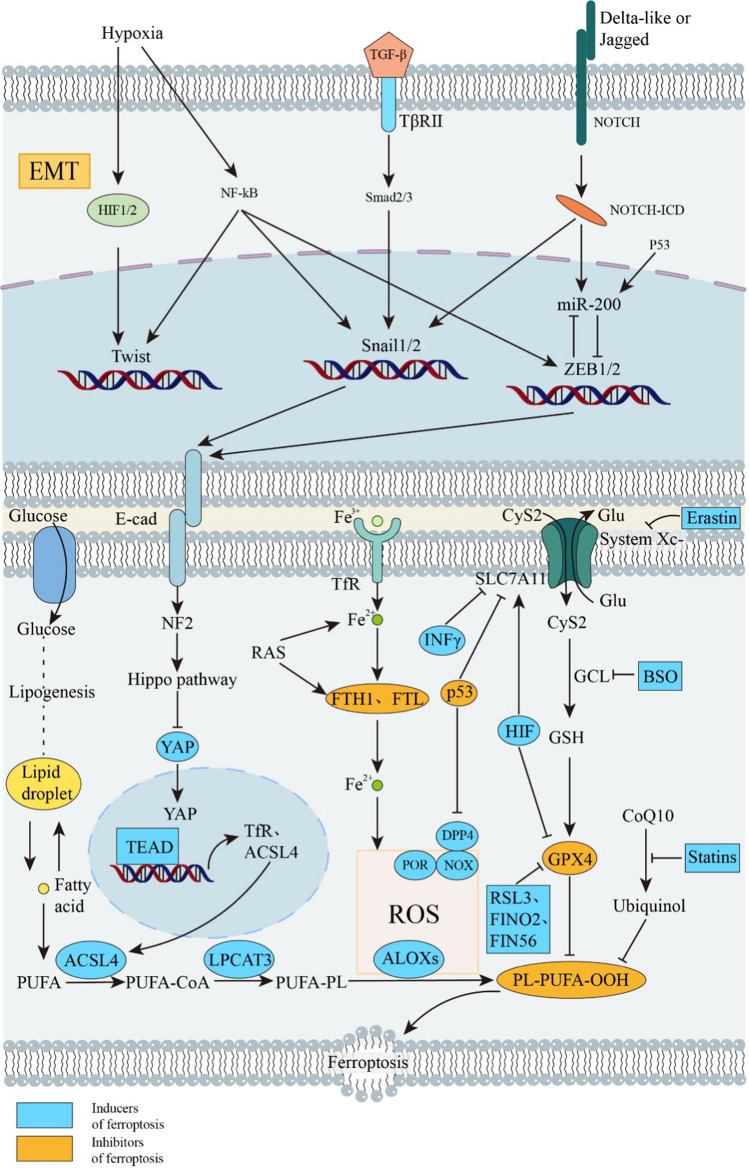
Fig. 1.
Cancer-related signaling pathways in ferroptosis and EMT. EMT and ferroptosis are associated with each other and tumorigenesis and development through RAS, TP53, hypoxia, TGF-β, and NOTCH-related pathways. Hypoxia, TGF-β, and NOTCH-related pathways affect transcription factors such as HIF, NF-κB, smad, etc., thereby affecting EMT-related transcription factors, including Twist, Snail, ZEB, and thus EMT. P53 also affects intranuclear miR-200 and thus the expression of the transcription factor ZEB. RAS affects ferroptosis by affecting lipid peroxidation by affecting ferritin components (FTH1 and FTL). P53 affects ferroptosis by affecting the Xc-system and lipid peroxidation. Inducers and inhibitors of ferroptosis are described by color in the figure. The blue and orange graphs represent inducers and inhibitors of ferroptosis, respectively. ZEB Zinc finger E-box binding, YAP yes-associated protein, TEAD TEA domain transcription factor, TfR transferrin receptor, FTH1 Ferritin Heavy Chain 1, FTL Ferritin Light Chain, Glu Glucose, CyS2 Cystine, BSO L-Buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine, RSL3 (1S,3R)-RSL3, FIN Ferroptosis inducers, E-cad E-cadherin, Erastin ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4, ALOXs lipoxygenases, CoA coenzyme A, CoQ10 coenzyme Q10, DPP4 dipeptidyl peptidase 4, FA fatty acid, G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, GCL glutamate-cysteine ligase, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, GSH glutathione, LPCAT3 lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3, NOXs NADPH oxidases, PL phospholipid, PLOOH phospholipid hydroperoxides, POR cytochrome p450 oxidoreductase