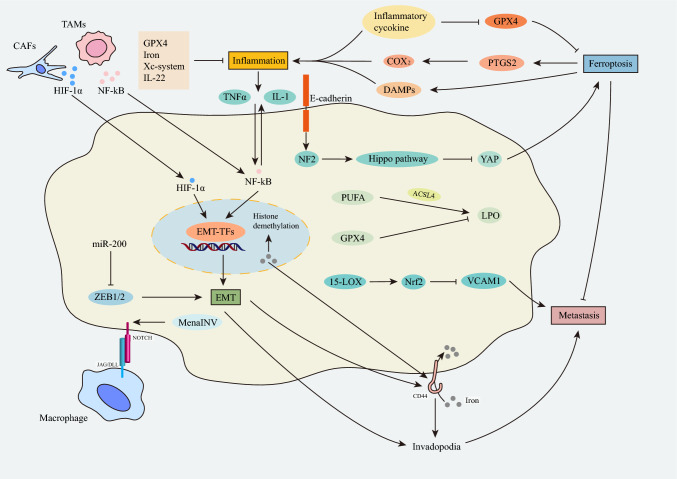
Fig. 2.
Crosstalk between ferroptosis and EMT in tumor inflammation and tumor metastasis. Genetic mutations in the E-cadherin-NF2-Hippo-YAP pathway sensitize cancer cells to ferroptosis and drive metastasis. GPX4 and 15-LOX inhibit tumor metastasis. Ferroptosis can directly increase the expression of PTGS2 of COX2, increase the secretion of inflammatory signals, and promote the occurrence of inflammation. Conversely, inflammation can also affect the occurrence of ferroptosis through the secretion of inflammatory factors. Inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-1 produced by inflammation, as well as HIF-1α and NF-κB produced by TAMs and CAFs, can indirectly affect the transcription factor expression of EMT. CAFs cancer-associated fibroblasts, TAMs Tumor-associated macrophages, LPO Lipid Peroxide, 15-LOX 15-lipoxygenase, MenaINV Mena invasive, PTGS2 Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2, VCAM1 Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1, Nrf2 NF-E2-related factor 2, DAMPs damage associated molecular patterns