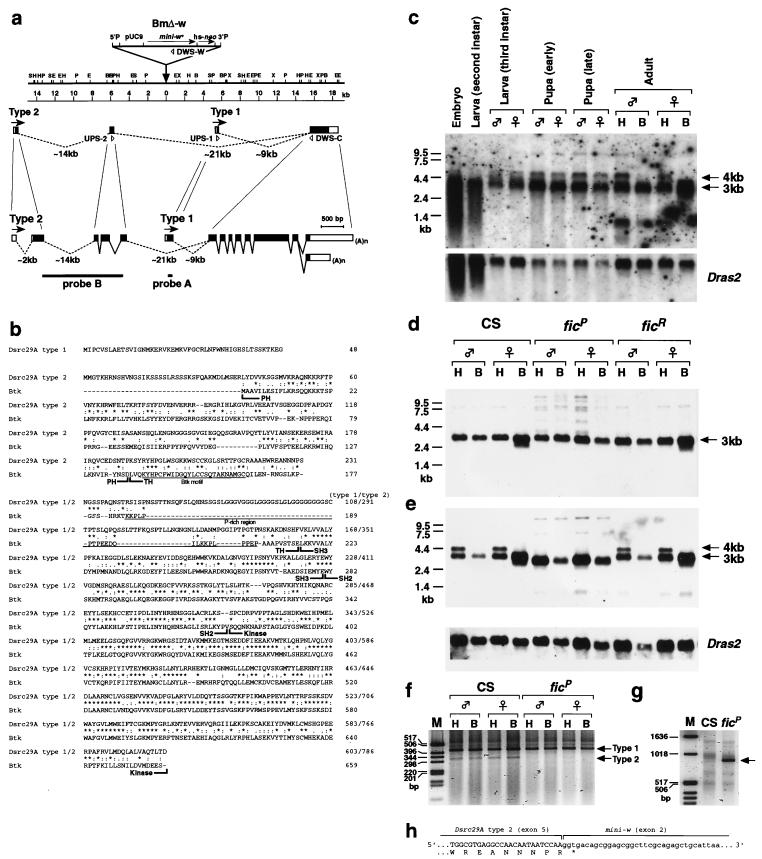
FIG. 3.
Molecular analysis of the Btk/Dsrc29A locus. (a) Restriction map of the chromosomal region defined by the ficP P-element insertion (indicated by a triangle). The Btk/Dsrc29A transcription unit is shown below the map. The direction of transcription is indicated by arrows. The exon-intron organization is illustrated below the map at two different scales. Open boxes represent noncoding regions; solid boxes represent coding regions; and lines represent introns. The sequences used as probes in Northern blot analysis are indicated by dotted lines at the bottom. The upstream primers (UPS-1 and UPS-2) and the downstream primers (DWS-C) for the PCR experiments are also shown. S, SacI; H, HindIII; P, PstI; E, EcoRI; B, BamHI; X, XbaI. (b) Primary structures of the Btk/Dsrc29A products deduced from the cDNA nucleotide sequences, and alignment of the amino acid sequence with that of human Btk. Identical residues are marked with asterisks. Conservative substitutions are dotted. The PH, TH, SH3, SH2, and kinase domains are indicated. The Btk motif and the proline-rich region are underlined. (c) Northern blot analysis of the developmental profile of Btk/Dsrc29A transcripts. The 4- and 3-kb mRNA species are expressed in embryos, second-instar larvae, third-instar larvae, and pupae. The 4-kb transcript is abundant in the head (H) but is not detectable in the body (B) of the adult flies. The blots were also hybridized with the Dras2 probe as a reference for the loading amount. (d) Comparison of the transcripts expressed in the adult stage between wild-type (CS), ficP, and a revertant, ficR. Probe A (see panel a) was used. (e) Similar comparison of the transcripts in CS, ficP, and ficR adults, detected with probe B (see panel a), which selectively hybridizes with the transcript having the PH domain-encoding region (i.e., type 2). ficP lacks two kinds of type 2 transcripts (i.e., the 3- and 4-kb transcripts), both having the 5′ sequence corresponding to the PH domain. These two transcripts are present in ficR and in the wild type. The 4-kb type 2 transcript is detectable only in the head part in wild-type and ficR flies. (f) PCR amplification of the type 1 and 2 products with CS and ficP RNA. Molecular size markers are shown in lane M. The primers used are as illustrated in panel a. The type 1-specific primer and the type 2-specific primer are expected to yield products of 426 and 324 bp, respectively (arrows). ficP lacks the type 2 product. (g) PCR amplification of CS and ficP RNA with the type 2-specific upstream primer and the mini-w-specific downstream primer. The product is detectable only in ficP (arrow). The size of the product (approximately 900 bp) matches the expected size when the 5′ half of type 2 RNA is spliced to the second exon of the mini-w gene in the P-element. (h) Sequence of the chimeric transcript composed of 5′ exons of type 2 and mini-w mRNA.