Figure 8. Angiopoietin-1 supplementation prevents C/EBPβ activation in hepatocytes.
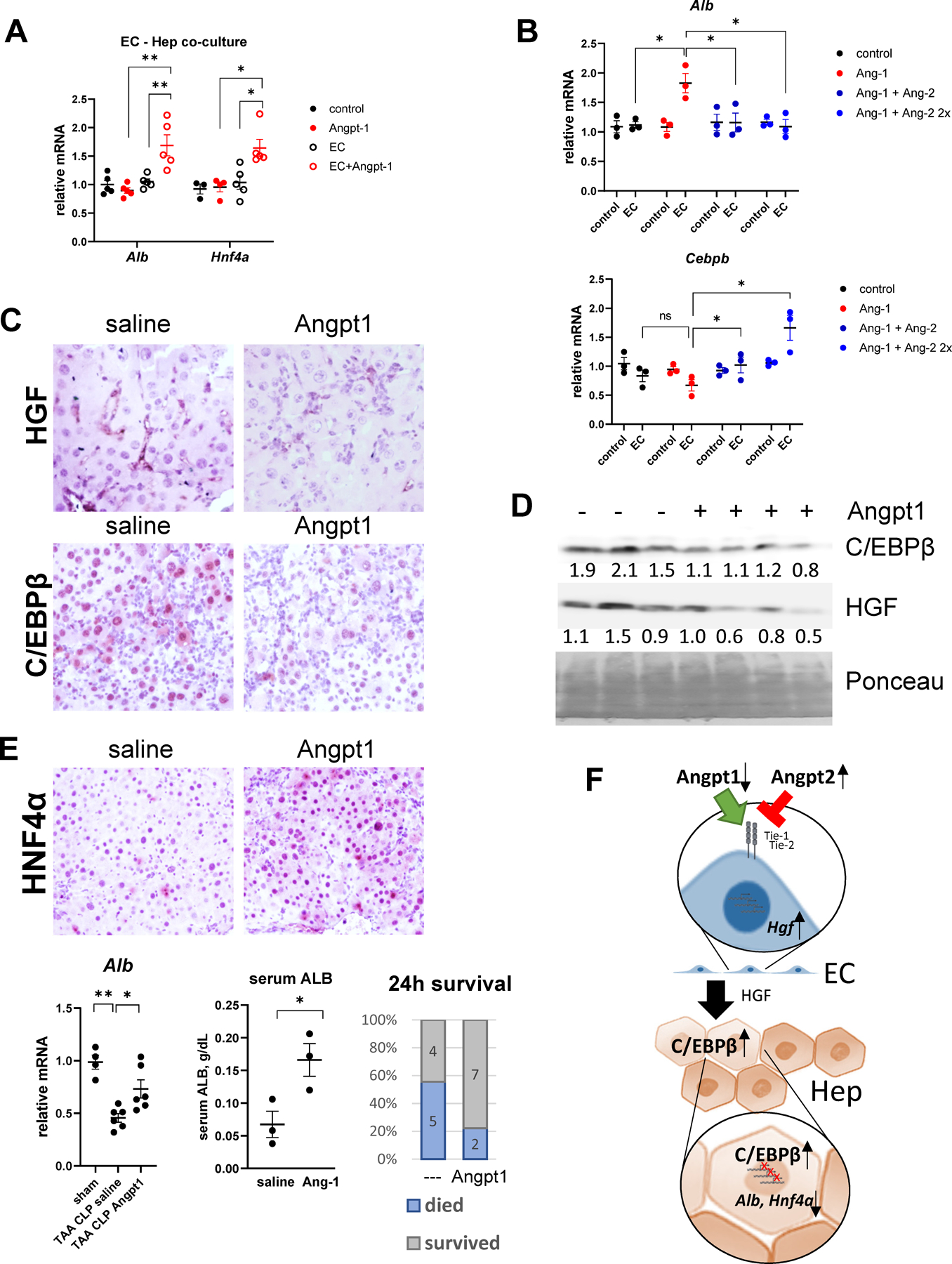
A. Primary mouse hepatocytes alone or in co-culture with LSECs were treated with recombinant Angiopoietin-1 (10 ng/ml). Relative gene expression. N=3–4 per group. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01. B. Primary mouse hepatocytes alone or in co-culture with LSECs were treated with recombinant Angiopoietin-1 (10 ng/ml) and Angiopoietin-2 (10 and 20 ng/ml). Relative gene expression. N=3 independent experiments. *, P<0.05 using paired ttest. C-E. TAA/CLP mice received 5 μg of recombinant Angiopoietin-1 or saline control at 2 hours after CLP. C. Liver section from indicated groups of mice at 24 hours post-CLP were stained using HGFα or C/EBPβ specific antibodies (total C/EBPβ). D. Western blot analysis of C/EBPβ and HGF protein levels in the livers. D. Whole liver mRNA gene expression and mortality in TAA/CLP mice. E. Top. Liver section from indicated groups of mice at 24 hours post-CLP were stained using HNF4α specific antibodies. Bottom. Albumin liver mRNA and serum levels and mortality at 24h. F. Proposed model of ACLF pathogenesis.
