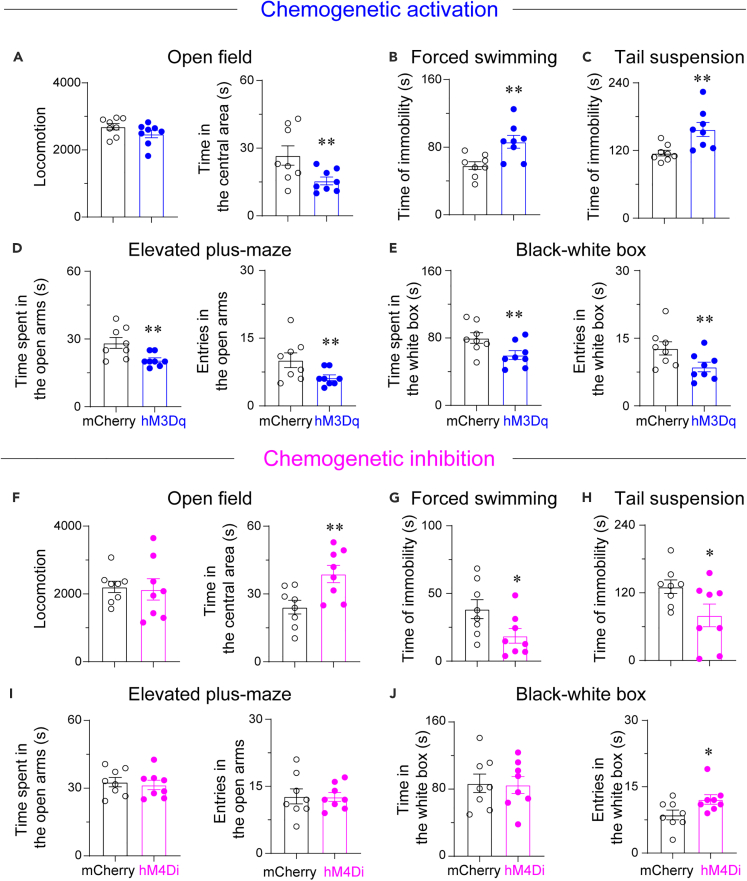
Figure 4.
VPVglut2 neurons exhibit activity-dependent regulation of depressive-like behaviors
(A) Chemogenetic activation of VPVglut2 neurons did not affect locomotion, but decreased time spent in the center of the open field test. Time of immobility was increased after chemogenetic activation of VPVglut2 neurons in both forced swimming (B) and TS (C) tests. (D) Chemogenetic activation of VPVglut2 neurons decreased time spent and entries in the open arms of the EPM test. (E) Chemogenetic activation of VPVglut2 neurons decreased time spent and entries in the white box of the black-white box test. n = 8 mice per group, ∗∗p < 0.01, unpaired t-test.
(F–J) Chemogenetic inhibition of VP glutamatergic neurons attenuated depressive-like behaviors. The following behavioral tests were used: open field (F), forced swimming (G), TS (H), EPM (I), and black-white box (J). n = 8 mice per group, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, unpaired t-test.