Fig. 7. D2C7+αCD40 therapy increases functional and tumor antigen-specific CD8+ TILs in WT mice and loses antitumor efficacy in cDC1-lacking Batf3−/− mice bearing gliomas.
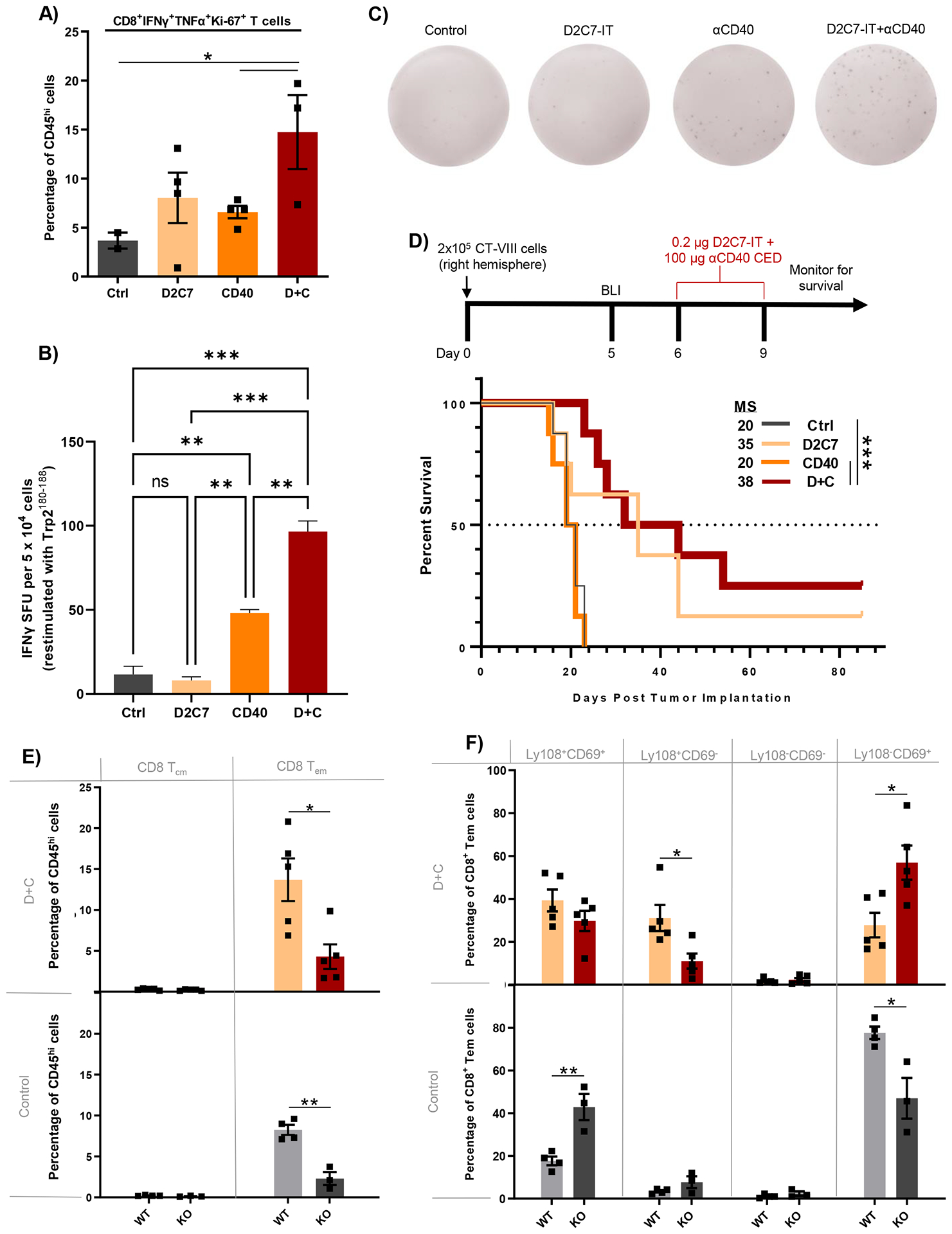
(A) FC analysis of CD8+IFNγ+TNFα+Ki-67+ T cells in CT-VIII tumor-bearing C57BL/6J WT mice, 6-days post Ctrl, D2C7, αCD40, and D+C therapies (n=2–4/group). (B) IFNγ ELISpot analysis performed on TILs harvested from CT-VIII-Trp2 tumors from C57BL/6J WT mice 6-days post-Ctrl, D2C7, CD40, and D+C therapies (n=3–6/group) stimulated with Trp2180–188 peptide. Background response from irrelevant peptide stimulation (< ~4 IFNγ spot forming units [SFUs]) subtracted from all plotted results. (C) Representative images of wells containing leukocytes isolated from Ctrl, D2C7, CD40, and D+C treated brains from C57BL/6J WT mice, and the IFNγ SFU observed following stimulation with Trp2180–188. (D) Survival of Batf3−/− (KO) mice implanted with CT-VIII (n=10/group) cells and treated with Ctrl, D2C7, αCD40, or D+C as indicated. (E-F) Frequencies of CD8+ T cells with central memory (Tcm) or effector memory (Tem) phenotype (E) and CD8+ Tem cells classified into specific exhaustion subset based on Ly108+ and CD69+ expression (F) in CT-VIII tumor hemispheres harvested 6-days post control or D+C therapy in WT and KO mice by FC analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. Data are mean ± SEM.
