Figure 6. Soluble histone protein promotes the degradation of histone mRNA in S phase.
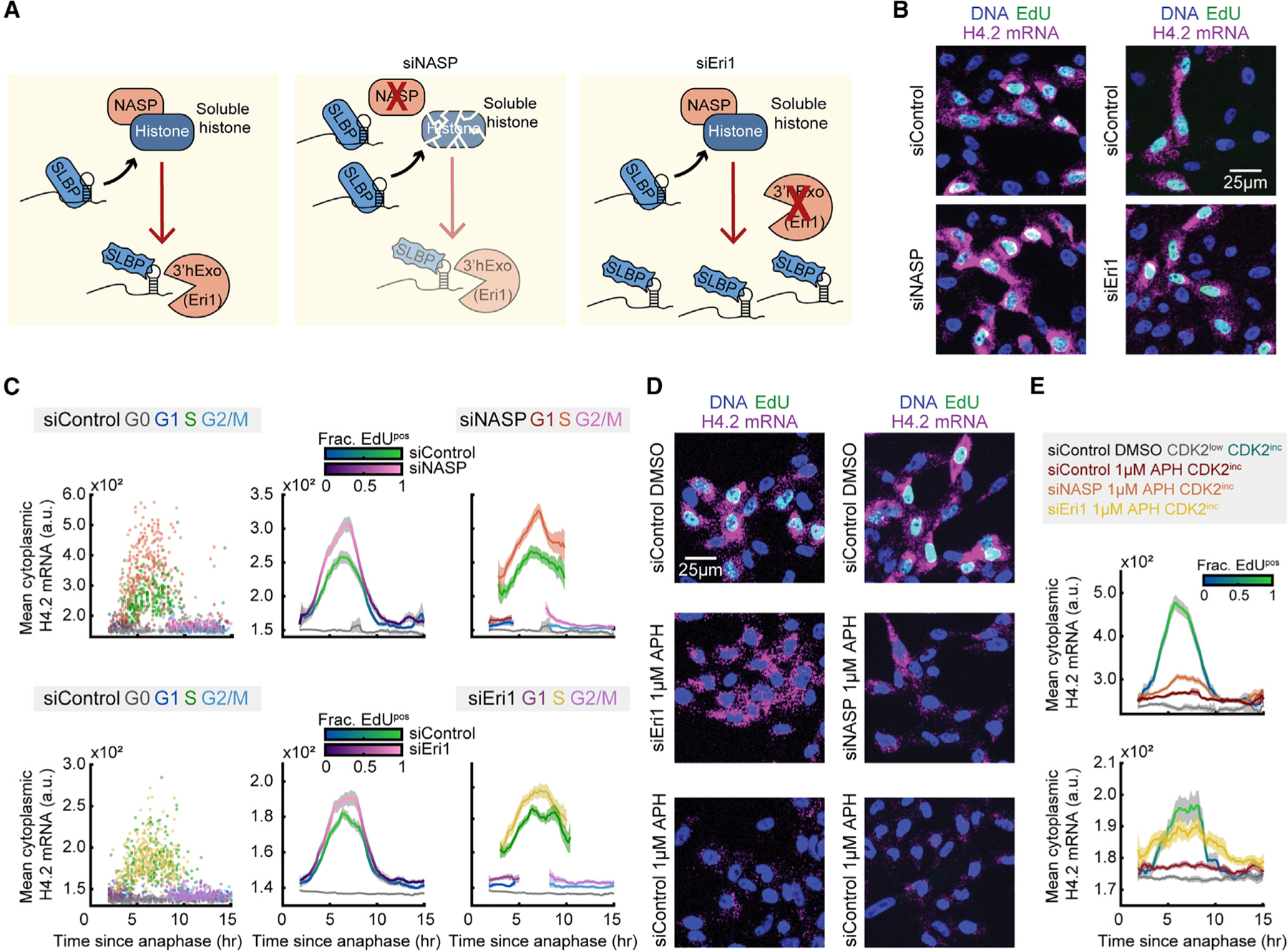
(A) Schematic of histone protein and histone mRNA stabilization with siRNA knockdown of NASP and Eri1. Soluble histone protein disrupts the interaction between SLBP and histone mRNA (squiggly SLBP), and Eri1 (3′hExo) is required for histone mRNA degradation.
(B) Representative images of cells treated with 20 nM siControl or siNASP for 24 h before fixation, or cells treated with 25 nM siControl or siEri1 for 48 h before fixation.
(C) Column 1: raw single-cell data. Column 2: mean cytoplasmic histone H4.2 mRNA signal and 95% confidence intervals as a function of time since anaphase for CDK2inc and CDK2low populations for cells treated with siControl vs. siNASP or siControl vs. siEri1. Column 3: CDK2inc population from column 2 segmented in to G1, S, and G2/M populations.
(D) Representative images of cells treated with 20 nM siControl for 24 h with 1 h of DMSO, 20 nM siControl for 24 h with 1 h of 1 μM APH, or 20 nM siNASP for 24 h with 1 h of 1 μM APH before fixation; and cells treated with 25 nM siControl for 48 h with 1 h of DMSO, 25 nM siControl for 48 h with 1 h of 1 μM APH, or 25 nM siEri1 for 48 h with 1 h of 1 μM APH before fixation.
(E) Mean histone H4.2 mRNA signal and 95% confidence interval for cells in (D), showing partial rescue of cytoplasmic histone H4.2 mRNA after APH treatment with siNASP or siEri1 knockdown.
Information on biological and technical replicates can be found in Table S2.
