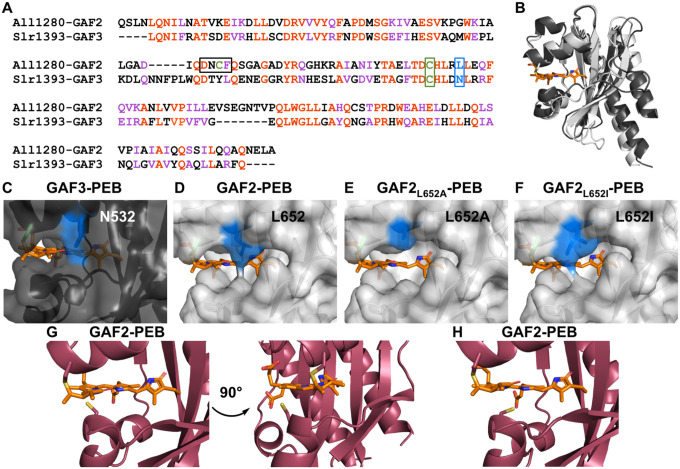
Figure 6.
Comparison of GAF proteins. A) Sequence alignment of All1280 GAF2 and Slr1393 GAF3. Amino acids are #441–596 from Slr1393 and #526–727 from All1280. The aligned residues are colored red and similar residues are colored purple. One of the residues mutated in GAF2 in this work (L652) is colored blue and outlined and the conserved cysteine residue (C648) that binds to the bilin in both GAFs is colored green and outlined. The corresponding residues are N532 and C528 in GAF3. The DXCF cysteine residue 620 found only in GAF2 is also highlighted green and the whole DXCF motif is outlined in the sequence alignment. B) Overlay of PyMOL representations of the crystal structure of Slr1393 GAF3-PCB (black, PDB 5DFX) and homology model of All1280 GAF2 (grey, prepared using SwissModel and based on PDB 6OAP). C–F) PyMOL models of the PEB binding site in C) GAF3, D) GAF2, E) GAF2L652A, and F) GAF2L652I. Mutations were modeled using the PyMOL mutagenesis wizard. The N532 side chain in GAF3 (C) and side chains in position 652 of GAF2 (D–F) are colored blue. G) Two views of the PyMOL representation of the PEB binding site in GAF2 (maroon, prepared using SwissModel and based on PDB 6MGH) shown with the nearby DXCF C620 residue. H) Depiction of an additional possible rotamer for C620 from part G that could place this residue even closer to the center of the bound bilin cofactor.