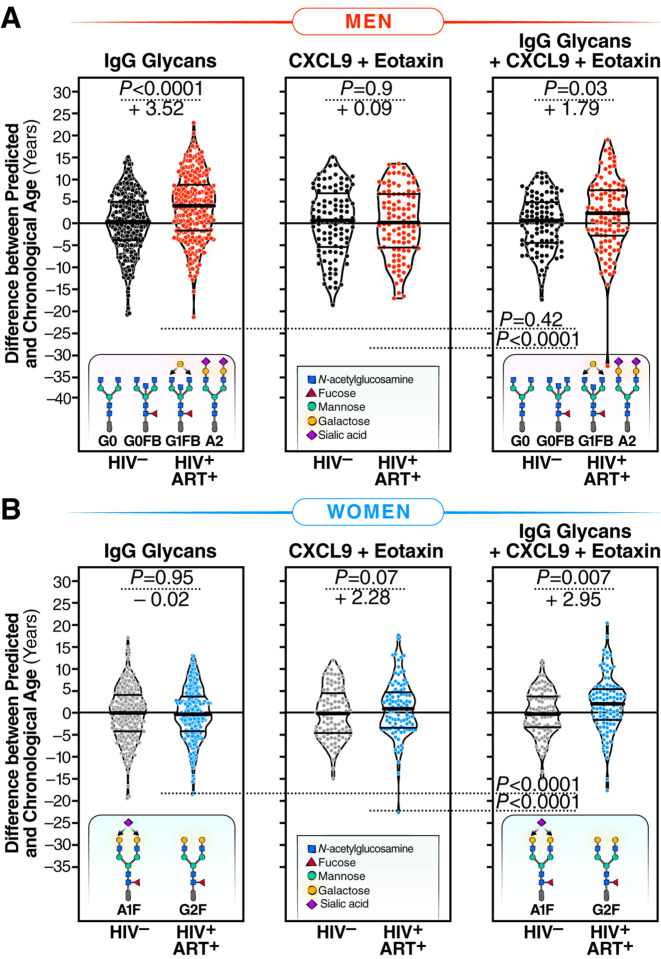
Figure 4. Machine-learning models based on IgG glycans indicate accelerated biological aging during HIV infection suppressed on ART.
(A) Four specific glycan traits were selected using the LASSO model and included in a model that correlated with chronological age in HIV-negative men, resulting in an average predicted age that closely matched chronological age. In MWH, the model revealed an average acceleration of 3.52 years between predicted and chronological age when compared to their HIV-negative counterparts. The left panel represents the model incorporating only these four glycans. The middle panel includes two inflammatory markers, CXCL9 and Eotaxin. The right panel combines the four glycan traits and the two inflammatory markers. Significance was determined using t-tests. The three models’ efficiency was evaluated using the likelihood ratio test for nested models. (B) Two specific glycan traits were selected using the LASSO model and included in a model that correlated with chronological age in HIV-negative women, resulting in an average predicted age that matched chronological age. The left panel represents the model incorporating only these two glycans. The middle panel includes the two inflammatory markers, CXCL9 and Eotaxin. The right panel combines the two glycan traits and the two inflammatory markers. In WWH, only the model combining glycans and inflammatory markers revealed an average acceleration of 2.95 years between predicted and chronological age. Significance was determined using t-tests. The efficiency of the three models was evaluated using the likelihood ratio test for nested models.