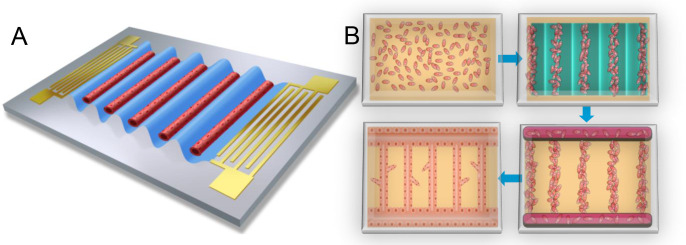
Figure 1.
Schematics of acoustofluidic engineering functional vessel-on-a-chip. A) As shown schematically, standing surface acoustic wave is generated on-chip to pattern the cells and promote the desired vessel formation. B) Flow chart of the acoustofluidic engineering of vessel formation. The suspended cells are patterned into the acoustic pressure node and aligned into parrel line array. After the acoustic field disappears, the solidified gel can still maintain the original patterning shape of the cells. Due to the nature of adherent growth, some excess vascular cells will grow along the wall of the PDMS chamber, forming transverse vessels perpendicular to the patterned longitudinal vessel tubes, thereby connecting these parallel arrays of vascular tubes. In the end, functional vessel-on-chip can be formed with the interstitial flow stimulation.