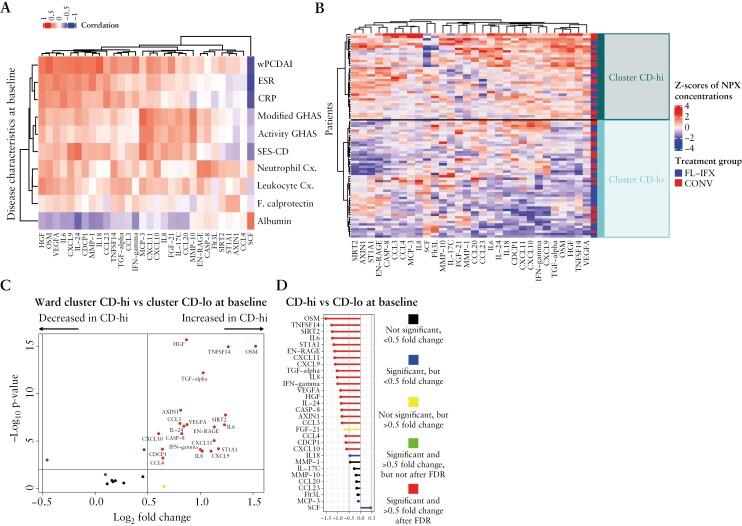
Figure 4.
Hierarchical clustering based on the baseline profiles of the 30 IFX-modulated proteins reveals two clusters of patients. [A] Heatmap of the Spearman’s correlation coefficient values between various clinical characteristics of CD and the serum concentrations of the 30 FL-IFX-modulated proteins at baseline [unpaired samples, n = 85]; wPCDAI, weighted paediatric Crohn’s disease activity score; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate [mm/h]; CRP, C-reactive protein [mg/L]; modified GHAS, modified global histological activity score; activity GHAS, activity global histological activity score; SES-CD; simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease; neutrophil Cx., neutrophil concentrations [109/L]; leukocyte Cx., leukocyte concentrations [109/L]; F. calprotectin, faecal calprotectin [µg/mL]; albumin, serum albumin [g/L]. [B] Heatmap with hierarchical clustering [Euclidean distance, Ward method] of the 30 IFX-modulated proteins at baseline [paired samples, n = 78] revealed two patient clusters: CD-hi, with a high inflammation profile, and CD-lo, with a lower inflammation profile. The proportions of patients receiving first-line infliximab [FL-IFX] and conventional treatment [CONV] were not significantly different between clusters [p = 0.535]. [C] Volcano plot showing the serum concentrations of 23 of the 30 FL-IFX-modulated proteins were significantly higher in the CD-hi cluster than CD-lo cluster at baseline [unpaired samples, n = 85; Mann–Whitney U-test]. [D] Comparison of the fold changes in the median serum concentrations of the 30 FL-IFX-modulated proteins between the CD-hi and CD-lo clusters after induction treatment. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant for all tests.