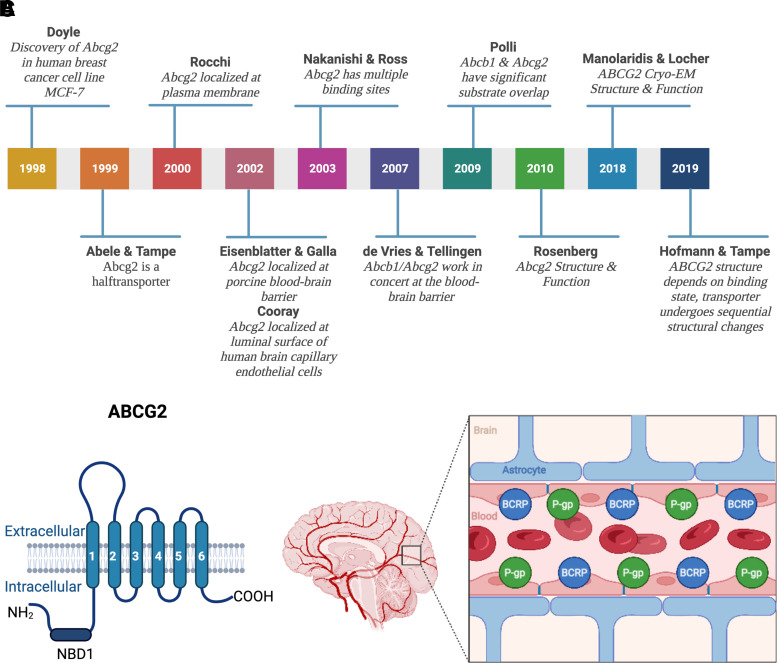
Fig. 3.
(A) History of ABCG2. From the discovery of the “breast cancer resistance protein” ABCG2 in 1998 to its cryo-EM structure and function. (B) ABCG2 structure. ABCG2 consists of one transmembrane domain that has six transmembrane spanning α-helices and one nucleotide binding domain (NBD1). ABCG2 is a half transporter that needs to homodimerize to fully function. (C) ABCB1 and ABCG2 at the blood-brain barrier. ABCB1 and ABCG2 are both located at the luminal membrane of endothelial cells comprising the blood-brain barrier. They act as a “first line of defense” by limiting xenobiotics including a large number of therapeutic drugs from entering into the brain. Created with BioRender.com.