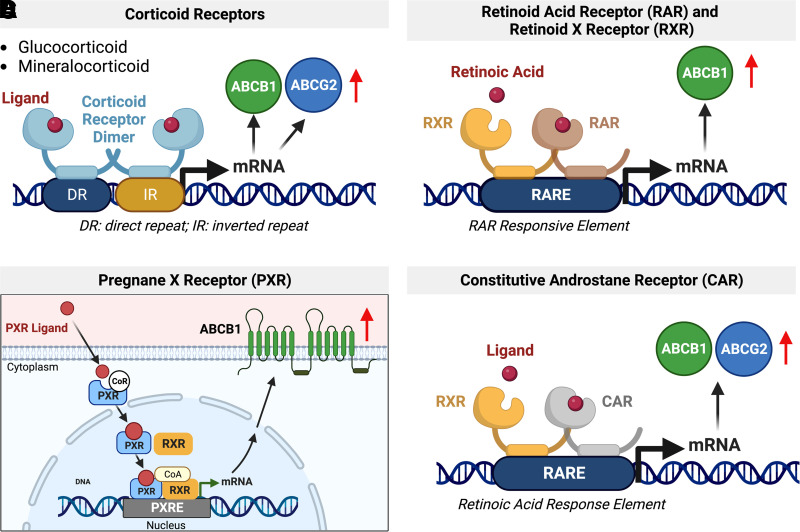
Fig. 5.
Regulation of ABCB1 and ABCG2 via corticoid receptors RAR/RXR, PXR, and CAR. (A) Upon ligand binding, the corticoid receptor dimer binds to the direct repeat and inverted repeat region of the target gene to increase ABCB1 and ABCG2 mRNA expression levels. (B) Upon ligand binding, RAR and RXR form a heterodimer that binds and activates the RAR response element (RARE), which increases ABCB1 expression. (C) A PXR ligand binds to inactivated PXR in the cytoplasm. Ligand binding then triggers conformational change of PXR during which the corepressor dissociates. Activated PXR translocates into the nucleus and heterodimerizes with retinoic X receptor α (RXRα). The complex PXR-RXRα together with its coactivators binds to the xenobiotic response element in the promotor region on ABCB1. This results in increased transcription of the gene and protein expression. (D) CAR forms a heterodimer with RXR that binds to RARE, which leads to an increase in ABCB1 and ABCG2 levels. Created with BioRender.com.