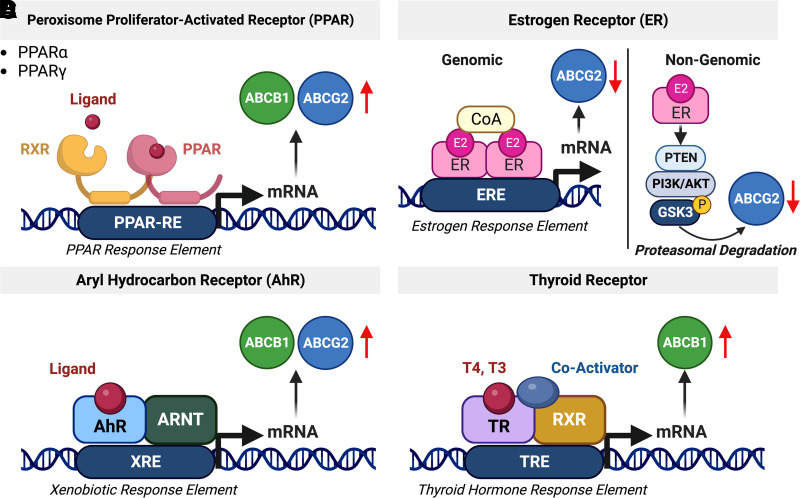
Fig. 6.
Regulation of ABCB1 and ABCG2 via the nuclear receptors PPAR, ER, AhR, and thyroid hormone receptor. (A) PPAR forms a heterodimer with RXR that binds to and activates the PPAR response element, which leads to increased ABCB1 and ABCG2 levels. (B) Genomic regulation of ABCG2 is driven by the estrogen receptor that binds to the estrogen response element in the ABCG2 promotor region. In addition, ABCG2 is also regulated via rapid, nongenomic ER signaling involving PTEN/PI3K/Akt/GSK3. (C) AhR translocates into the nucleus and dimerizes with the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator resulting in the regulation of its target genes, including ABCB1 and ABCG2. (D) The thyroid receptor forms a complex with RXR and coactivators. This complex binds to the thyroid hormone response element and activates transcription of ABCB1. Created with BioRender.com.