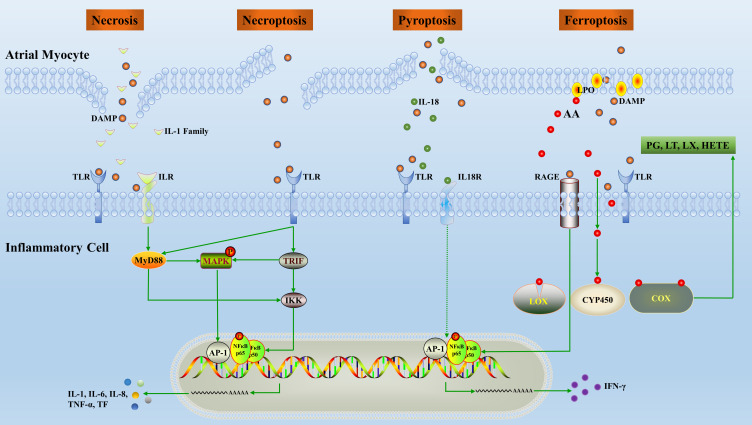
Figure 2.
Overview of the inflammatory pathways induced by inflammatory cell death. Release of inflammatory factors, mainly DAMPs, following cardiomyocytes death promotes polarization and chemotaxis of inflammatory cells. In turn, inflammatory cells secrete inflammatory factors which alter the structure and electrical conduction activity of the local microenvironment.
Abbreviations: AA, arachidonic acid; TF, tissue factor; AP, activating protein; NF, nuclear factor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; PG, prostaglandin; LT, leukotriene; LX, lipoxin; CYP450, cytochrome P450; MyD, myeloid differentiation factor; LOX, lipoxygenase; COX, cyclooxygenase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IKK, inhibitor of kappa B kinase; TLR, toll-like receptors; LPO, lipid hydroperoxide; DAMP, damage-associated molecular patterns; RAGE, the receptor of advanced glycation end products; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon β.