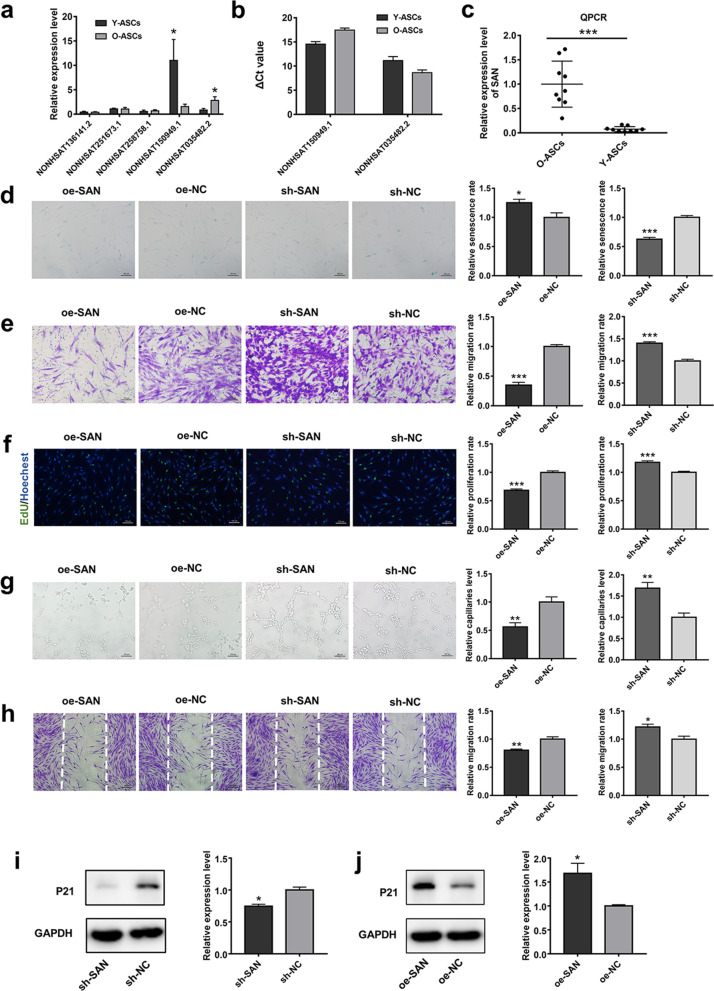
Fig. 1.
SAN expression patterns and effects of SAN in ASCs. a Validation of the five most altered lncRNAs by PCR analysis. n = 5. b ΔCT values of two significant altered lncRNAs. ΔCT = CT value (lncRNA)—CT value (GAPDH). n = 5. c The expression of SAN was then measured in O-ASCs and Y-ASCs. n = 10. d SA-β-gal staining and quantitative analysis of SA-β-gal-positive cells were conducted in cells subjected to SAN overexpression and knockdown. Scale bar = 100 µm. e Images of migrated cells and quantitative analysis of ASCs transduced with sh-NC, sh-SAN, oe-NC, or oe-SAN. Scale bar = 100 µm. f Representative images and quantitative analysis of EdU-stained cells (green) in ASCs that received the above treatment; nuclei were stained blue. Scale bar = 100 µm. g Images of tube formation and analysis of HUVECs treated with CM from ASCs in the above four groups. Scale bar = 100 µm. h Images and analysis of migrated fibroblasts treated with CM as described above. Scale bar = 200 µm. i Western blotting and quantitative analysis of the expression levels of p21 in ASCs transduced with sh-NC or sh-SAN. j Western blotting and quantitative analysis of the expression levels of p21 in ASCs transduced with oe-NC or oe-SAN. n = 3. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. All experiments were performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus sh-NC group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus oe-NC group. ns, not significant