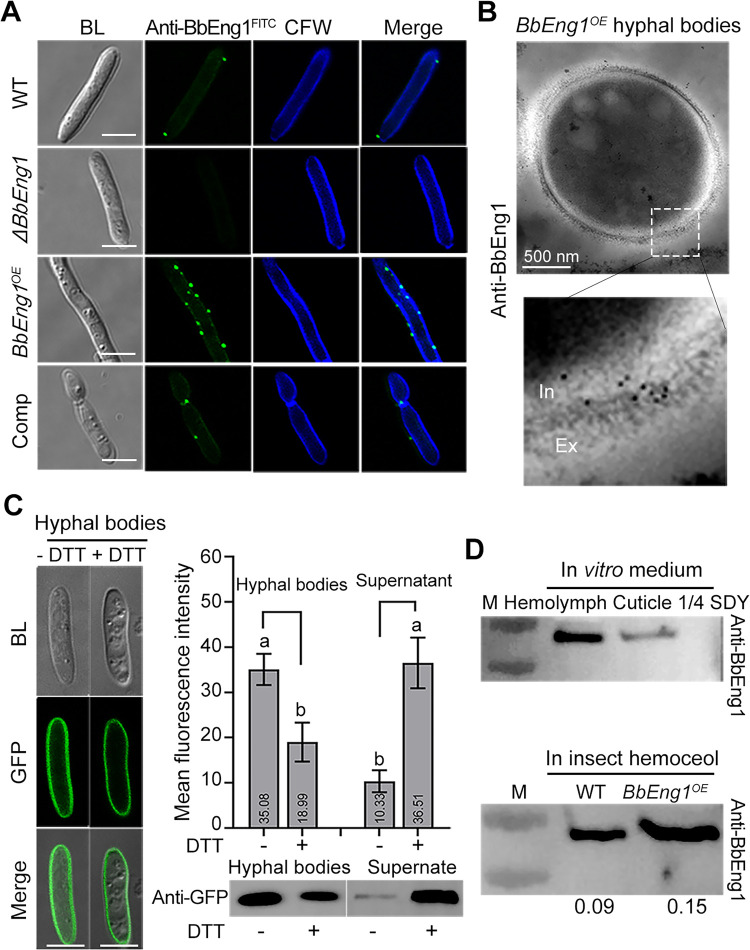
Fig 2. Distribution and secretion of BbEng1 in B. bassiana.
A. Indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) images (scale: 5 μm) examining subcellular localization of BbEng1 in B. bassiana wild-type, ΔBbEng1, BbEng1OE and complementation (Comp) hyphal bodies probed with anti-BbEng1 polyclonal antibody and FITC-conjugated-goat anti-rabbit IgG. Fungal cell wall was stained with CFW (calcofluor white). B. Immuno-transmission electron images of BbEng1 in hyphal bodies of BbEng1OE probed with anti-BbEng1 polyclonal antibody and anti-Rabbit IgG (Whole molecule)-Gold. C. Microscopic images (scale: 5 μm) of BbEng1::GFP expressed in hyphal bodies after 12-h treatment with 2 mM dithiothreitol (DTT). Left, GFP fluorescence in fungal cells. Right, fluorescence density in the supernatant. The BbEng1::GFP cells and the supernatant were probed with anti-GFP antibody. Control (-), not treated with DTT. Error bars: SDs. Different letters indicate significant differences pairs (P < 0.01, t-test). D. Western blotting detection of secreted BbEng1 by anti-BbEng1 polyclonal antibody. Upper, wild-type incubated 12 h in insect-derived nutrient-contained broth (0.167 g / L silkworm cuticle; 5 mL / L silkworm hemolymph) and 1/4 SDY broth. Lower, insect hemolymph of larvae after 48-h injection with wild-type and BbEng1OE conidia. The digital values denote the amount of BbEng1 secreted by the tested strains in the host hemolymph.