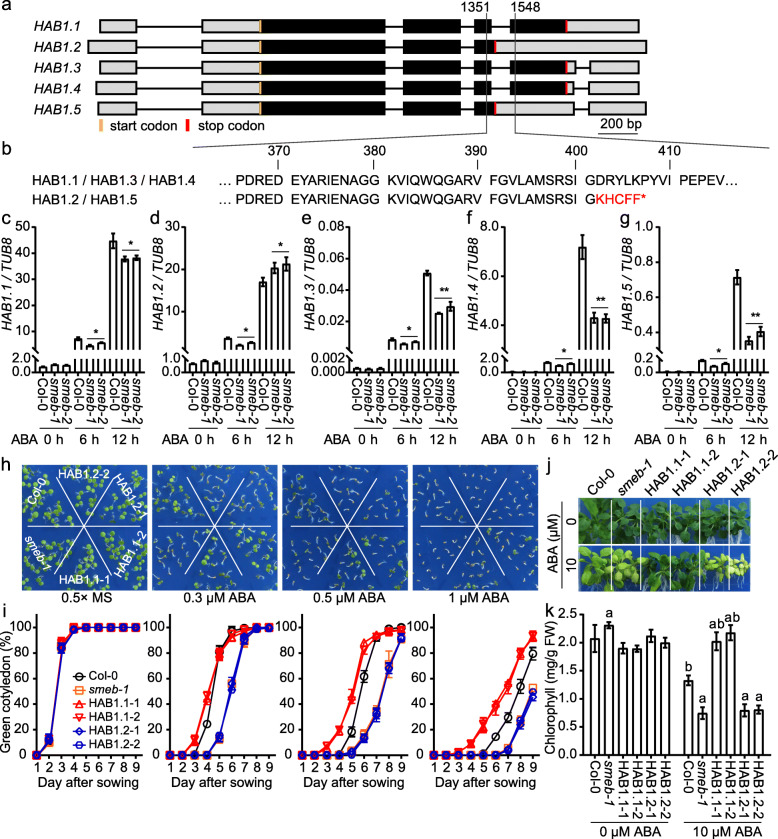
Fig. 2.
SmEb modulates the alternative splicing of HAB1 in response to ABA. a Different alternative splicing variants of HAB1 as determined by sequence analysis of cloned PCR products. The lines between boxes indicate introns. The grey and black boxes represent the UTR and exon, respectively. b Amino acid sequence resulting from alternative splicing and the formation of a full-length and truncated HAB1 proteins in the close-up view. HAB1.1, HAB1.3 and HAB1.5 encode the full-length HAB1 protein, while the HAB1.2 and HAB1.4 encode the truncated HAB1 protein. c-g Relative transcript levels of different alternative splicing variants of HAB1 in Col-0, smeb-1 and smeb-2 plants subjected to 50 μM ABA for 0, 6, or 12 h, as determined by qRT-PCR analysis. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3), * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, Student’s t-test. h Cotyledon greening assay of Col-0, smeb-1, HAB1.1-1, HAB1.1-2, HAB1.2-1, and HAB1.2-2 after seed sowing for 6 days in 0.5× MS medium containing 0, 0.3, 0.5, or 1 μM ABA. HAB1.1-1 and HAB1.1-2, two independent lines of smeb-1 expressing 35S:HAB1.1-3 × FLAG transgene. HAB1.2-1 and HAB1.2-2, two independent lines of smeb-1 expressing 35S:HAB1.2-3 × FLAG transgene. i Percentages of green cotyledon of Col-0, smeb-1, HAB1.1-1, HAB1.1-2, HAB1.2-1, and HAB1.2-2 after seed sowing for indicated days in 0.5× MS medium supplementing 0, 0.3, 0.5, or 1 μM ABA. Error bars represent ± SD (n = 6). j Seven-day-old Col-0, smeb-1, HAB1.1-1, HAB1.1-2, HAB1.2-1, and HAB1.2-2 seedlings grown in 0.5× MS medium were transferred to 0.5× MS medium with or without 10 μM ABA and grown for an additional 3 weeks. k The chlorophyll content of rosette leaves of Col-0, smeb-1, HAB1.1-1, HAB1.1-2, HAB1.2-1, and HAB1.2-2 plants shown in (j). Values are mean ± SD (n = 6). The letters a and b above the columns indicate a significant difference relative to Col-0 and smeb-1 mutant, respectively (P < 0.05, Student’s t-test)