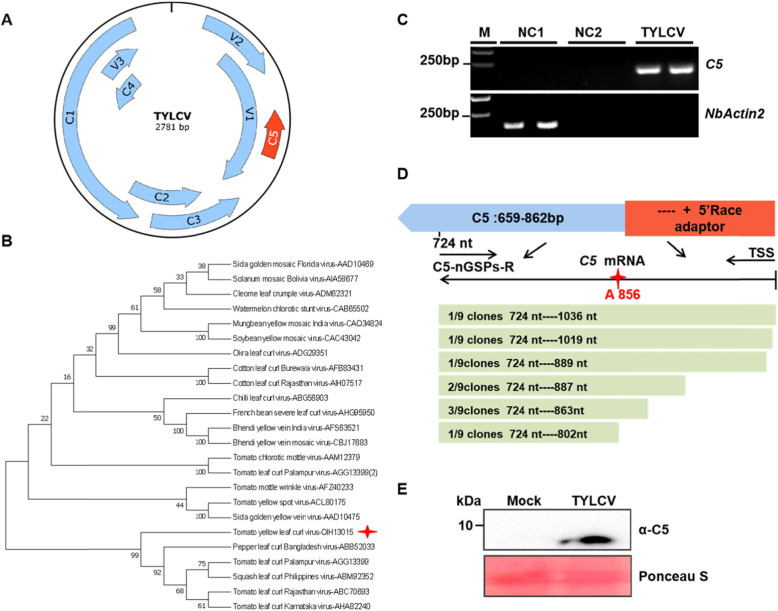
Fig. 1.
Sequence analyses of the TYLCV C5 protein. A Schematic representation of the TYLCV genome. B Phylogenetic analysis of C5 amino acid (aa) sequences of representative begomoviruses. The amino acid sequences of C5 proteins from 23 begomoviruses viruses were aligned using by ClustalW method with MEGA7. C RT-PCR analysis of C5 transcripts from TYLCV-infected or mock-inoculated N. benthamiana plants. M: DNA ladder marker. NC1: negative control 1 (reverse-transcription of total RNA extracted from the mock-inoculated plants with RT Primer mix of random 6 mers and oligo dT primer. NC2: negative control 2 (reverse-transcription of total RNA extracted from the mock-inoculated plants with C5-specific primers). TYLCV: reverse-transcription of total RNA extracted from the TYLCV-infected plants with C5-specific primers. C5: PCR products of C5 with a pair of C5-specific primers. NbActin2: PCR products of NbActin2 with a pair of NbActin2-specific primers. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results; representative images are shown. D Transcriptional start site analysis of TYLCV C5 by 5′ RACE. TSS: transcription start site. A856: C5 TSS was captured by RSV cap-snatching (Lin et al., 2017). E Western blot analysis of total protein from the TYLCV-infected N. benthamiana leaves at 72 hpi with anti-C5 antibodies, Mock: N. benthamiana plants infiltrated with an A. tumefaciens clone containing the pCambia 2300 vector. Three plants were analyzed for each treatment. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Ponceau S staining of the large RuBisCO subunit serves as loading control