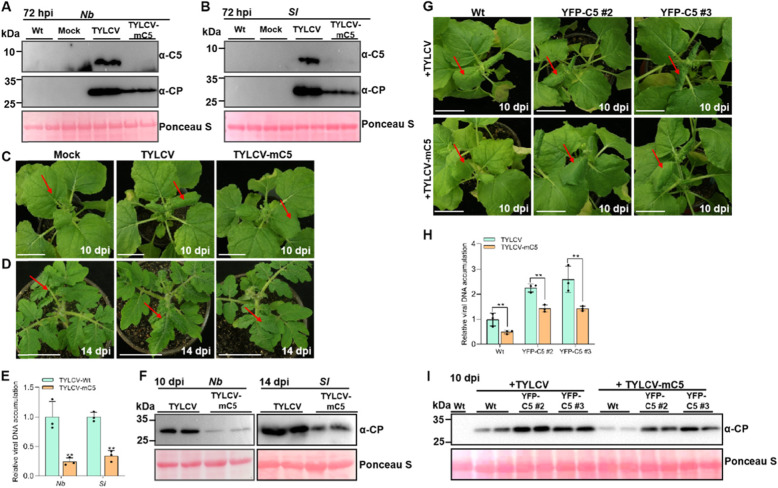
Fig. 6.
C5 is important for TYLCV infection in N. benthamiana and S. lycopersicum plants. A-B Western blot analyses of TYLCV C5 and CP protein accumulation with specific anti-C5 and anti-CP antibodies in local leaves of TYLCV- and TYLCV-mC5-inoculated plants of N. benthamiana (Nb) (A) or in cotyledons of TYLCV- and TYLCV-mC5- infected plants of S. lycopersicum (Sl) (B). Wt: uninoculated plants; Mock: inoculated plants with pCambia 2300 vector; TYLCV/TYLCV-mC5: inoculated plants with the infectious clones of TYLCV/TYLCV-mC5. Ponceau S staining of the large RuBisCO subunit serves as loading control. C Symptoms of N. benthamiana plants inoculated with Mock, TYLCV, or TYLCV-mC5 infectious clones at 10 dpi. Bar = 4 cm. D Symptoms of tomato plants inoculated with Mock, TYLCV, or TYLCV-mC5 infectious clones at 14 dpi. E Western blot analyses of TYLCV CP accumulation in systemic leaves of TYLCV- and TYLCV-mC5- infected plants from (C and D). Ponceau S staining of the large RuBisCO subunit serves as loading control. F qPCR analysis of the viral DNA accumulation of TYLCV or TYLCV-mC5 -infected plants from (C and D). Three plants were analyzed for each treatment and this experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent ± SD (n = 3) and 25S RNA was used as the internal reference. G Symptoms of YFP-C5 transgenic N. benthamiana plants infected with TYLCV or TYLCV-mC5 at 10 dpi. Bar = 4 cm. H Western blot analyses of TYLCV CP accumulation in systemic leaves of TYLCV- and TYLCV-mC5-infected plants from (G). Ponceau S staining of the large RuBisCO subunit serves as loading control. I qPCR analysis of the viral DNA accumulation of TYLCV or TYLCV-mC5 -infected plants from (G). Three plants were analyzed for each treatment and this experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent ± SD (n = 3). Student’s t test was used to statistically analyze each group of data, and double asterisks indicate significant statistical differences (**p < 0.01) between two treatments