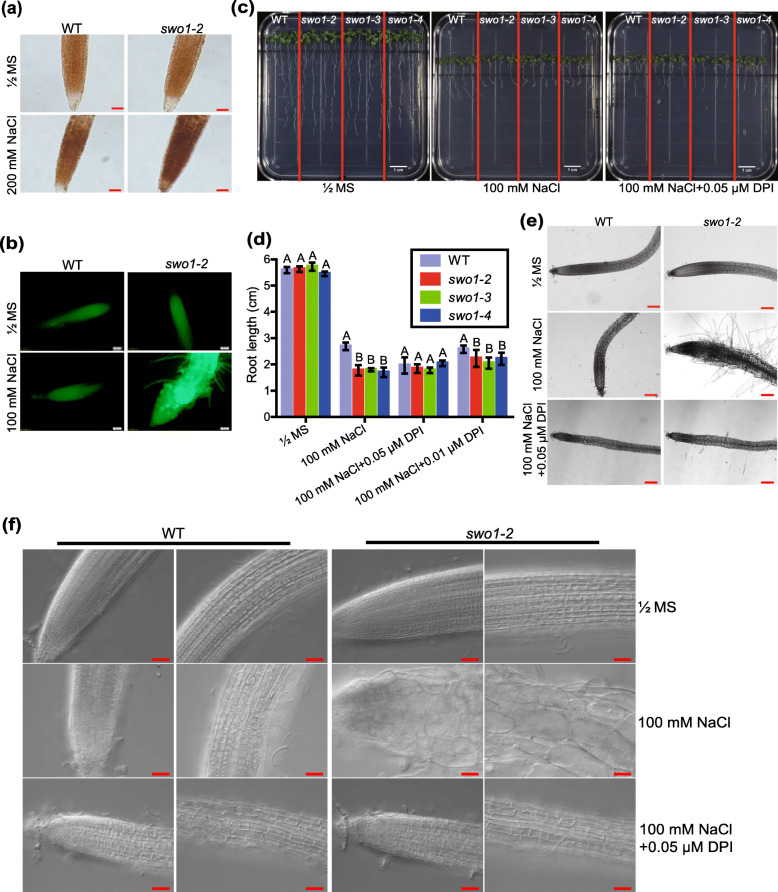
Fig. 4.
ROS accumulation is responsible for salt stress-triggered root cell swelling in swo1 mutant. (a) DAB staining of H2O2 in the roots of the wild type and swo1–2 mutant. The upper panel shows the staining of the roots grown under normal conditions, and the lower panel shows the staining of the roots treated with 200 mM NaCl for 6 h. Scale bar = 50 μm. (b) Analysis of ROS level by H2DCF-DA staining. Four-day-old seedlings of the wild type and swo1–2 were transferred to MS media supplemented with or without 100 mM NaCl for 10 days. Roots were stained with H2DCF-DA and fluorescent signals were detected using an Olympus DP72 microscope. Scale bar = 100 μm. (c) Root phenotypes of the wild type and swo1 mutants after being transferred to MS, MS + NaCl (100 mM), and MS + NaCl+DPI (0.05 μM) media for 7 days. (d) Quantification of the root lengths of the wild type and swo1 mutants after being transferred to MS, MS + NaCl (100 mM), MS + NaCl+DPI (0.05 μM), and MS + NaCl+DPI (0.01 μM) media for 7 days. Data are means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters represent significant differences between different genotypes under the same treatment, P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA). (e) Morphology of the root tips of the wild type and swo1–2 after being transferred to MS, MS + NaCl (100 mM), and MS + NaCl+DPI (0.05 μM) media. The left panel shows the images of the wild type and the right panel shows the roots of swo1–2. Scale bar = 200 μm. (f) DIC images show the root cell morphology of the wild type and swo1–2 grown on MS, MS + NaCl (100 mM), and MS + NaCl+DPI (0.05 μM) media for 7 days. Scale bar = 50 μm