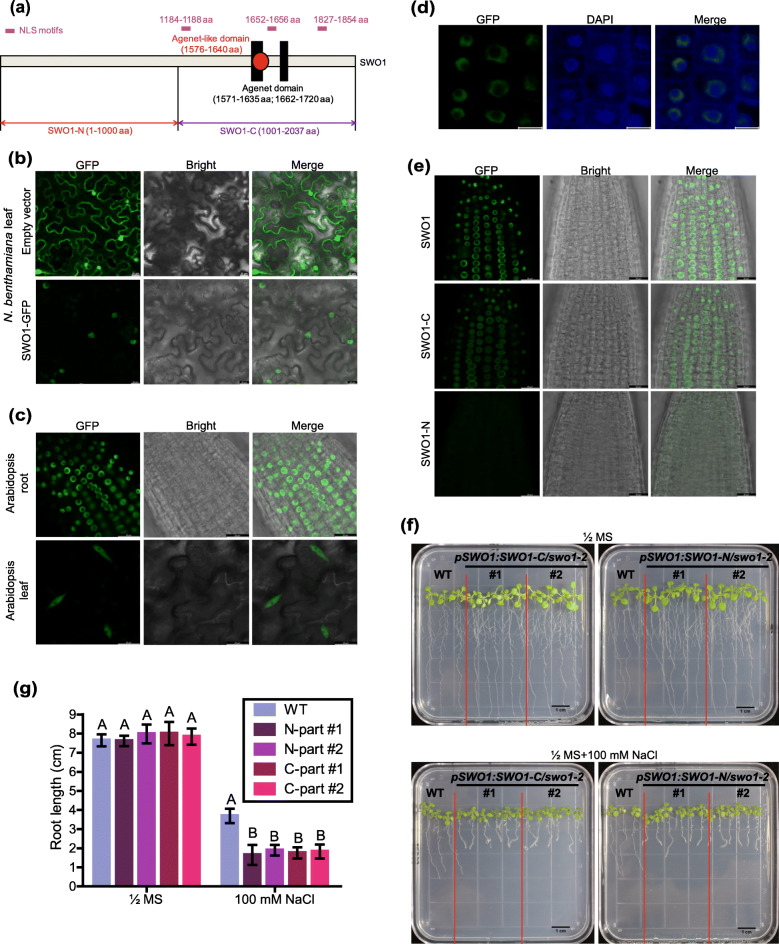
Fig. 7.
Both N- and C-termini are required for the function of SWO1 in the regulation of salt tolerance. (a) Schematic diagram shows the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of SWO1 protein. Black rectangles and red dot represent plant Agenet and Agenet-like domains, respectively, with the corresponding amino acid positions in the parentheses. The positions of the three NLS motifs are marked in purple. The fragments of SWO1-N and SWO1-C are also indicated in the diagram. (b) Subcellular localization of SWO1 in N. benthamiana leaves. The leaves expressing free GFP were used as control. Scale bar = 20 μm. (c) Subcellular localization of SWO1 in Arabidopsis roots (upper panel) and leaves (bottom panel). Scale bar = 20 μm. (d) Overlay between SWO1-GFP and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) staining in Arabidopsis roots. Scale bar = 10 μm. (e) Subcellular localizations of the full-length and truncated SWO1 proteins in Arabidopsis roots were detected by confocal microscopy. Scale bar = 20 μm. (f) Four-day-old seedlings of the wild type and transgenic plants expressing the N-terminal or C-terminal domain of SWO1 in swo1–2 mutant background were transferred to MS and MS + NaCl (100 mM) media. The photographs were taken 7 days after transfer. (g) Quantification of the root lengths of the wild type and transgenic plants expressing truncated SWO1 after being transferred to MS and MS + 100 mM NaCl media. Data are means ± SD (n = 6). Different letters represent significant differences between different genotypes under the same treatment, P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA)