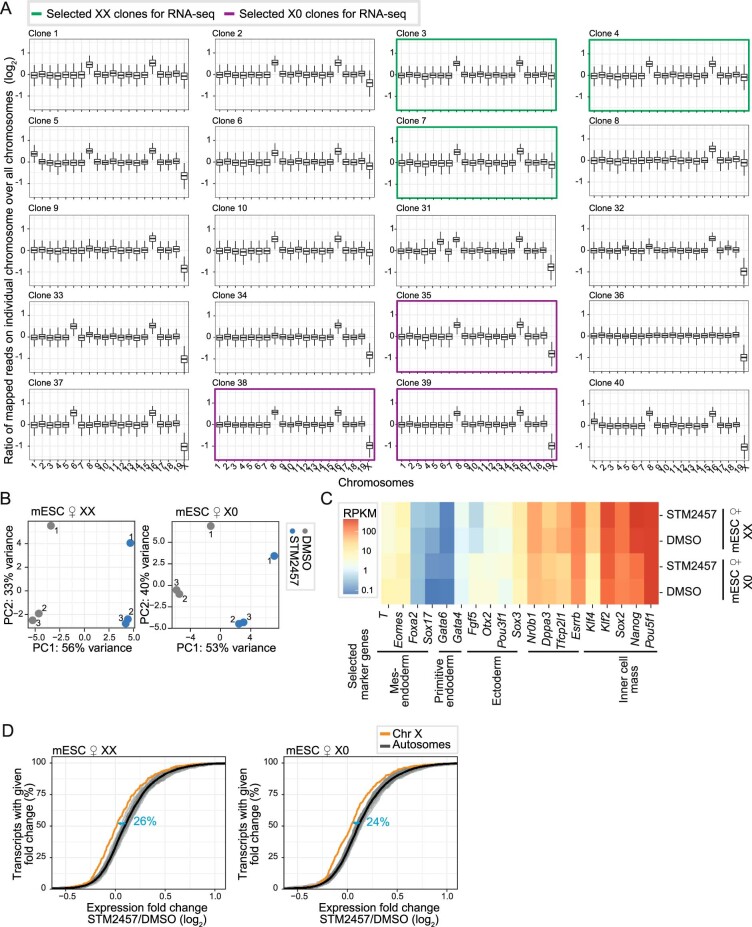
Extended Data Fig. 9. X-chromosomal and autosomal transcripts differ in their response to m6A depletion in both XX or X0 clones of female mESC.
a. The majority of clones lost one copy of the X chromosome (X0). 20 single colonies of female mESC were picked and cultured under standard conditions until confluency was reached. To determine chromosome copy number, DNA-seq reads were counted into 100 kb bins along the chromosome and divided by the median mapped reads of all bins along the genome. Shown is the distribution of the resulting ratios for the bins on each chromosome. Six clones that were selected for RNA-seq in control and m6A-depleted (STM2457, 9 h) condition are highlighted in green. Boxes represent quartiles, centre lines denote 50th percentiles (medians), and whiskers extend to most extreme values within 1.5× interquartile range. b. Principal component analysis of RNA-seq replicates from female X0 (left) and XX (right mESC clones under m6A-depleted (STM2457, 9 h) and control conditions. Analysis based on numbers of reads for the 500 genes with highest variance across all samples. c. Expression levels (RNA-seq) of marker genes confirm the pluripotent state of the female XX and X0 mESC under m6A-depleted (STM2457, 9 h) and control conditions. Expression is shown as RPKM (mean over replicates, log10). d. X-chromosomal transcripts are less upregulated than autosomal transcripts upon m6A depletion in female X0 and XX mESC (P value = 3.51e-11 [mESC X0], P value = 1.64e-12 [mESC XX], two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Cumulative fraction of transcripts (RPKM > 1) on individual autosomes (grey) and the X chromosome (orange) that show a given expression fold change (log2, RNA-seq) upon m6A depletion (STM2457, 9 h). Mean expression changes for all autosomes are shown as black line. Effect sizes (blue) shown the shift in medians, expressed as percent of the average IQR of autosomal and X-chromosomal transcripts (see Methods).