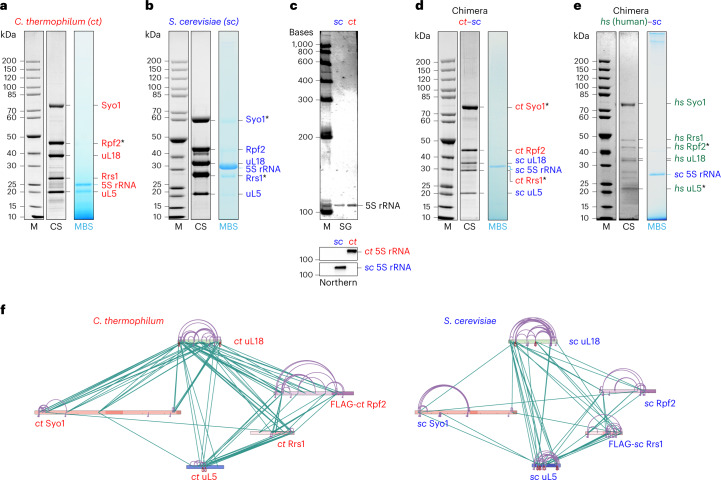
Fig. 1. Isolation of hexameric 5S RNP complexes from Chaetomium thermophilum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and reconstitution of thermophile–yeast and human–yeast 5S RNP chimeras.
a, Affinity purification of C. thermophilum (ct) 5S RNP via ctRpf2. b, Split-tag affinity purification of S. cerevisiae (sc) 5S RNP via scSyo1–scRrs1 pair. c, SYBR Green II staining (SG) to detect the total RNA and northern blot analysis (Northern) of ct and sc 5S rRNA extracted from the isolated 5S RNP complexes and probed with sc-specific and ct-specific 5S rRNA oligonucleotide probes. d, Split-tag affinity purification of the thermophile–yeast 5S RNP (ct–sc chimera) via ctSyo1–ctRrs1 pair. e, Split-tag affinity purification of the human–yeast 5S RNP (hs–sc chimera) via hsuL5–hsRpf2 pair. The final eluates from a, b, d and e were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie staining (CS). Labeled bands were identified by mass spectrometry or by methylene blue staining (MBS) to reveal the 5S rRNA. One caveat of SDS–PAGE/MBS staining is that the structured 5S RNA may not be fully denatured by SDS, causing different running behavior. To correctly analyze the 5S RNA, we also performed denaturing urea PAGE of the 5S RNP samples from sc and ct (see Fig. 1c). A protein molecular-weight marker standard (M) is shown on the left for the SDS–PAGE gels (a,b,d,e). An RNA molecular-weight standard (indicated in bases) is shown for the urea PAGE gel (c). Asterisks indicate the baits used for each affinity purification step. All purifications were done at least twice with a similar outcome. f, XL-MS of the affinity-purified 5S RNP from C. thermophilum (left) and S. cerevisiae (right) using DSS-H12. The protein primary structures of Syo1, uL18, uL5, Rpf2 and Rrs1 are shown, and specific regions are indicated in darker colors. Intermolecular crosslinks are shown in green, and intramolecular crosslinks are shown in purple. The xiNET tool45 was used for visualization.