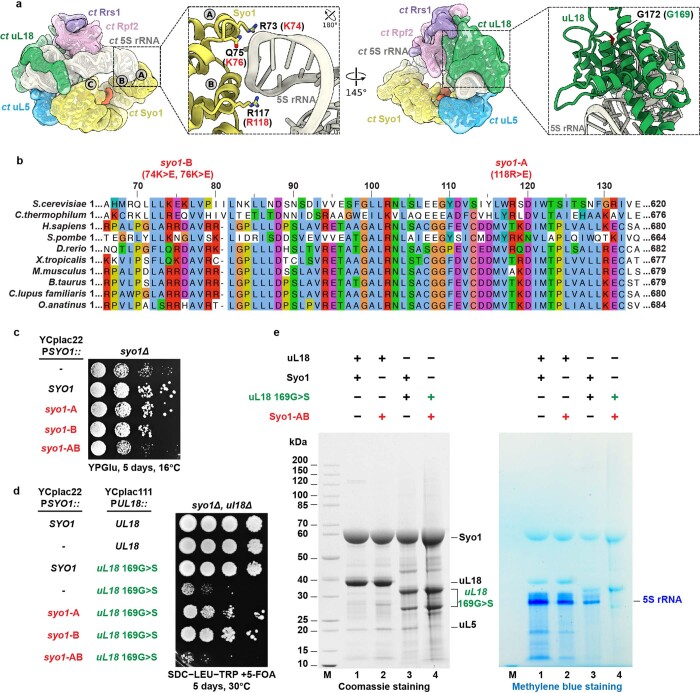
Extended Data Fig. 4. Structure-based mutations in Syo1 mapping at the contact site to 5S rRNA helix IV.
a, Overview and zoomed-in view of the ct 5S RNP cryo-EM structure showing contact of Syo1 N-terminal end to the 5S rRNA tip in the region of helix IV. Sites A and B correspond to regions in the Syo1 N-terminal domain with direct contact to the 5S rRNA. The residues of sites A and B for ctSyo1 are labeled in black and the corresponding residues in yeast Syo1 in red. Site C corresponds to a region in C-terminal domain of Syo1 that is also in close proximity to the 5S rRNA. Highlighted is also residue G169 of S. cerevisiae uL18 (G172 in C. thermophilum), which upon mutation yields a slow-growing yeast mutant (see also panel D). b, Multiple sequence alignment of the Syo1 N-terminal region, indicating the positively charged amino acids at the 5S rRNA contact sites: K74 and K76 (termed syo1-B) and R118 (termed syo1-A). These sites were mutated to glutamic acids. c, Dot–spot growth analysis of the syo1∆ strain transformed with plasmid-borne SYO1, syo1-B (74K>E, 76K>E), syo1-A (118R>E), and the combination syo1-AB (74K>E, 76K>E, 118R>E). Growth analyses have been performed twice with a similar outcome. d, Synthetic lethality relationship between syo1-AB and uL18 169G>S mutant alleles. The yeast syo1∆ uL18∆ double-disruption strain (carrying wild type uL18 on pRS316-URA3) was transformed with plasmids carrying either uL18 or uL18 169G>S in combination with plasmids carrying either empty (-), SYO1 or the indicated syo1 mutant alleles. This genetic experiment has been repeated twice with a similar outcome. e, Split-tag affinity purification of overexpressed Syo1 or Syo1-AB mutant (both ProtA-TEV-tagged) in combination with uL18 or uL18 169G>S (both FLAG-tagged). The final eluate was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining to reveal Syo1 and uL18 (left panel), and methylene blue staining to visualize the 5S rRNA (right panel). The uL18 169G>S mutant protein is partially degraded, yielding two smaller breakdown products verified by mass spectrometry. This co-immunoprecipitation assay has been performed twice with a similar outcome.