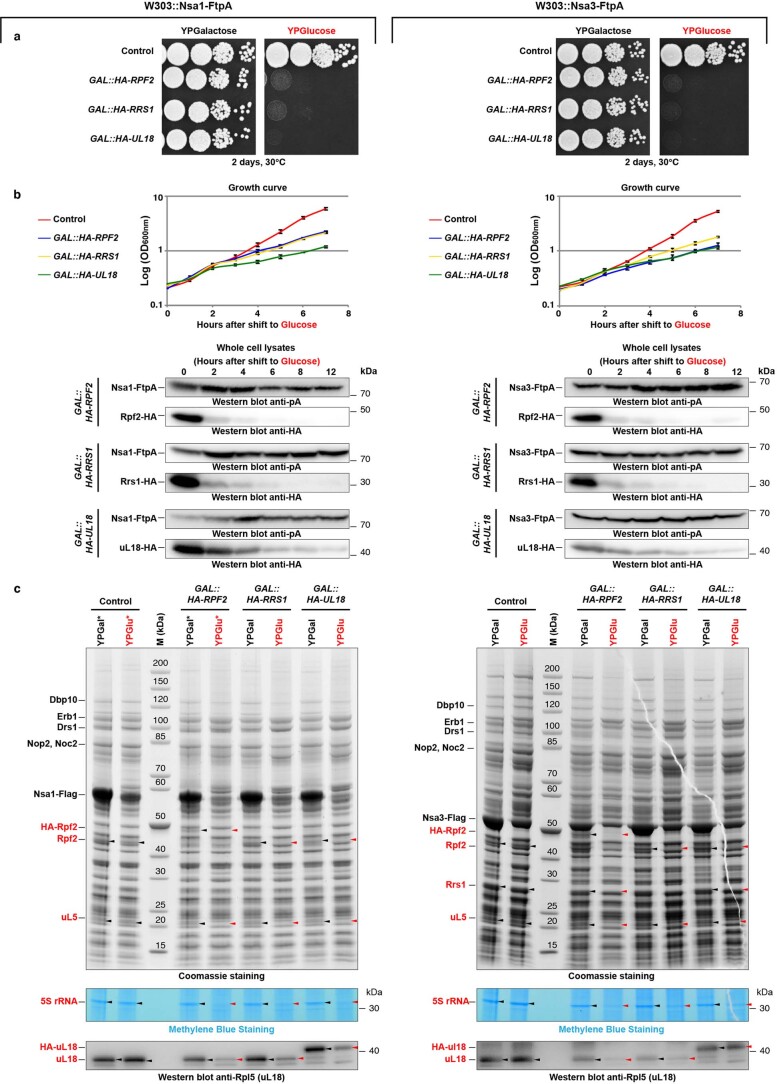
Extended Data Fig. 5. In vivo depletion of the yeast 5S RNP from pre-60S particles by GAL promoter-driven repression of either GAL::HA-RPF2, GAL::HA-RRS1 or GAL::HA-uL18.
a, b, Yeast strains (W303) carrying genomically integrated FLAG-TEV-ProtA tag fused at the C-terminus of either NSA1 (left) or NSA3 (right), each under control of the endogenous promoter. Dot–spot (a) and liquid culture (b) growth analysis of the indicated yeast strains on galactose (inducing) and glucose (non-inducing) containing medium. Samples were collected at the indicated hours and whole lysates were analyzed by western blot (lower panel) to follow the depletion of the indicated gene constructs. The growth curves show the mean ± STD of 3 replicas per culture. c, SDS-PAGE analysis of pre-60S particles isolated via tandem affinity purification based FtpA-tagged bait constructs (left: Nsa1-FtpA; right, Nsa3-FtpA) of the corresponding yeast strains, grown after 6 hours in either glucose or galactose containing medium. Black arrows point to the 5S RNP factors, and red arrows to the verified depletion (analyzed by mass spectrometry) of these factors. Labeled bands were identified by mass spectrometry. Staining with methylene blue revealed the 5S rRNA, and uL18 was detected by Western blot. Total YPGal and YPGlu eluate samples marked with asterisks were analyzed by SQ-MS. (Source Dataset 2; see also Fig. 3a, left panel). These depletion experiments have been done at least twice for all the groups with consistent results, and the Rpf2-depletion was further used as routine for the production of pre-60S particles depleted of 5S RNP.