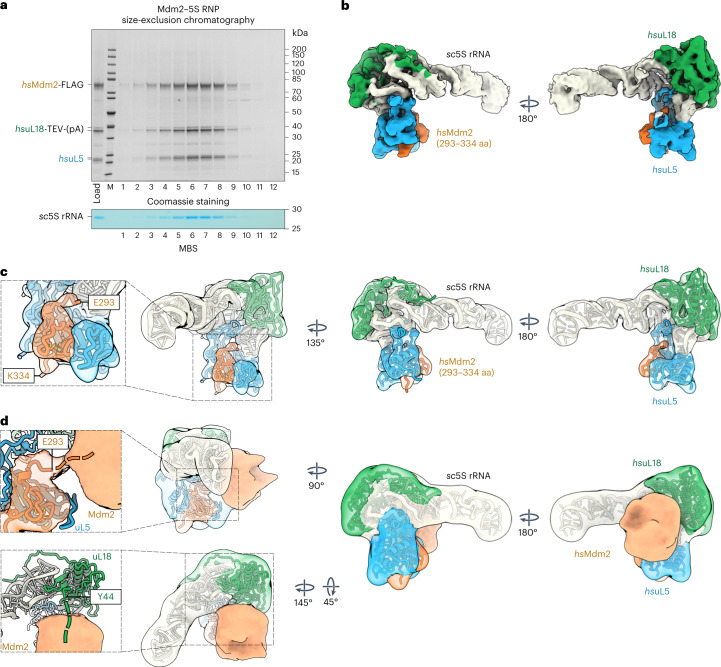
Fig. 5. Reconstitution and cryo-EM structure of the Mdm2–5S RNP complex.
a, Split-tag affinity purification of the reconstituted Mdm2–5S RNP complex (hsMdm2–hsuL18–hsuL5–sc5S rRNA) using hsuL18-TEV-ProtA as first bait and hsMdm2-FLAG as second bait, followed by size-exclusion chromatography. The final eluate (Load) and fractions 1–12 from the gel-filtration column were analyzed by SDS–PAGE. Labeled bands were identified by mass spectrometry. The gel was also stained with MBS to reveal the 5S rRNA. The purification of the Mdm2–5S RNP complex was performed more than five times with similar outcomes. b,c, Cryo-EM map (b) and fitted model (c) of the Mdm2–5S RNP complex (PDB IDs 4XXB for Mdm2, 6ZM7 for hsuL5 and hsuL18, and 3JCT for sc5S rRNA). aa, amino acids. The components of the complex are shown in different colors and labeled. d, Model and Gaussian filtered map of the Mdm2–5S RNP complex refined without mask and at lower contour levels revealing additional Mdm2 electron density. The appearing flexible density (unresolved parts of Mdm2) contacts the N-terminal residue E293 of the Mdm2 zinc finger domain, as well as the uL18 N-terminal residue Y44 (expansions, left). The connections of the Mdm2 zinc finger and the unresolved N terminus of uL18 are indicated with dashed lines.