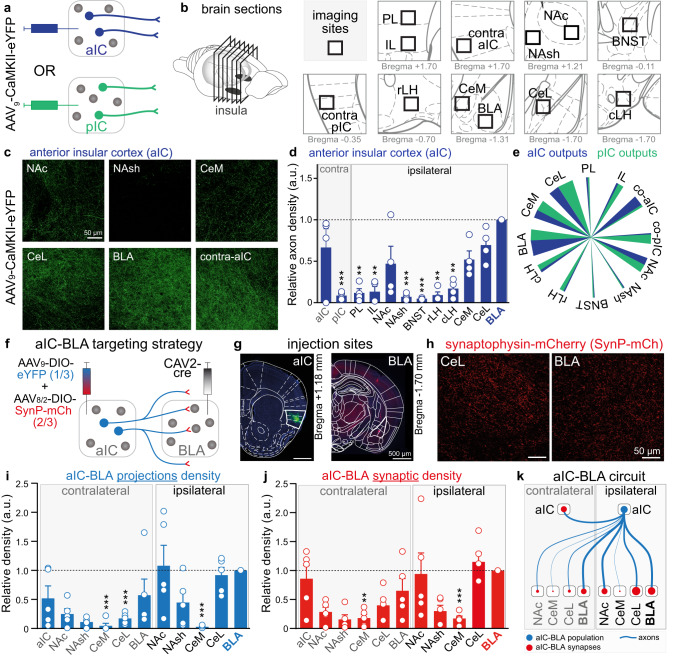
Fig. 3. Downstream projections of anterior insula neurons and aIC-BLA collaterals.
a, b Experimental scheme of viral expression a and imaging downstream regions b, including prelimbic (PL), infralimbic (IL) cortices of the medial prefrontal cortex, contralateral aIC (contra-aIC), contralateral pIC (contra-pIC), nucleus accumbens core (NAc), nucleus accumbens shell (NAsh), bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), rostral lateral hypothalamus (rLH), caudal lateral hypothalamus (cLH), basolateral amygdala (BLA), medial (CeM) and lateral (CeL) subdivisions of central amygdala. c Representative images of axonal projections from one mouse expressing eYFP in glutamatergic aIC neurons. d Number of fluorescent pixels normalized to the average value of the maximal projection region (BLA) per image from aIC neurons (n = 4 mice). The two bar graphs on the left represent the contralateral aIC and pIC relative axonal density (One-way ANOVA, *p = 0.0198, Bonferroni test compared to BLA image **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). e Summary pie chart of relative fluorescent intensity in projecting regions from aIC (blue) and pIC (green). f Viral vector strategy to target aIC to BLA collaterals with eYFP labelling the axonal density and synaptophysin-mCherry (SynP-mCh) targeting synaptic inputs. g Representative images of aIC (left) and BLA (right) transfected with a cre-dependent dual-viral vector and CAV2-cre respectively. h Representative confocal images of SynP-mCherry in the CeL and the BLA. i, j. Number of fluorescent pixels representing aIC to BLA axonal i and synaptic j density normalized to the average value of the ipsilateral BLA image (n = 5 mice). (One-way ANOVA, i *p = 0.0193, Bonferroni test compared to ipsi-BLA image **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; j **p = 0.0095, Bonferroni test compared to ipsi-BLA image **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). k Summary of the aIC-BLA circuit including ipsilateral and contralateral projections. Blue represents the aIC-BLA population and the red dots represent aIC-BLA synapses. The width of the lines is proportional to the axonal density and the size of the red dots is proportional to the number of synaptic inputs. All the results are represented as mean ± SEM.