Figure 4.
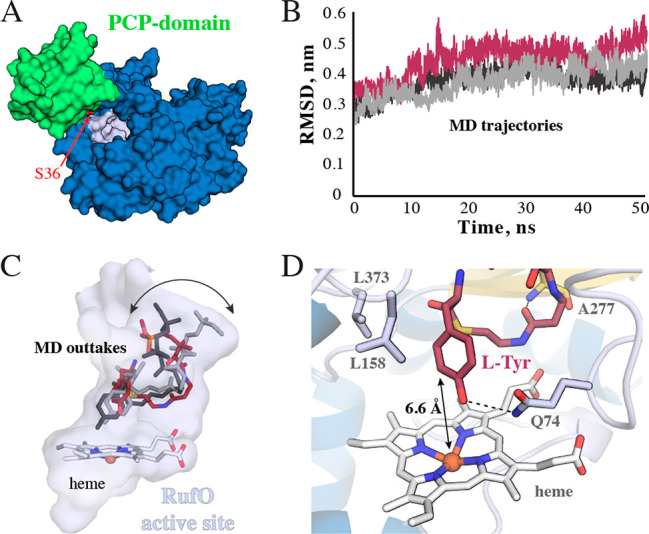
Computational prediction of the RufO substrate complex. (A) Surface model of the apo PCP domain bound to RufO. We highlight the serine that is ultimately phosphopantetheinylated in red. (B) Time-evolution RMSD plots of three independent 50 ns MD simulations of RufO in complex with the docked phosphopantetheinyl arm covalently linked to l-Tyr. (C) Snapshots of the three trajectories bound in the RufO active site pocket. Variation is primarily observed where the arm would attach to the PCP domain. (D) Representative configuration of the PCP-bound l-Tyr primed for the nitration reaction. The distance between the Fe ion and C3 is highlighted, as are key hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts. See Figure S14 for a more complete interaction diagram. Secondary structure elements are colored as in Figure 1.
