Figure 2.
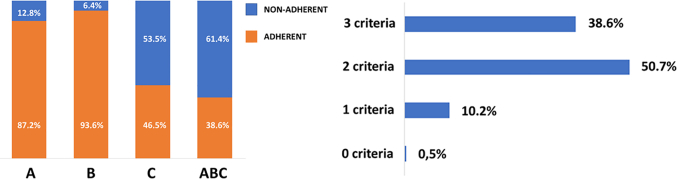
ABC Criteria Adherence and Distribution
The ABC pathway has 3 main pillars: “A” for avoiding stroke with oral anticoagulation; “B” refers to symptom control; and “C” for management of cardiovascular risk factors. The patient was considered compliant for the “A” criterion if properly prescribed with oral anticoagulation according to the CHA2DS2-VASc score. Any patient with no symptoms or with mild symptoms not affecting daily life was qualified for the “B” criterion. A patient was considered adherent to the “C”" criterion when hypertension, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, heart failure, stroke or transient ischemic attack, and diabetes mellitus were treated according to the current clinical guidelines. All patients with ≥1 clinical condition not properly treated were considered to be “C”" criterion nonadherent. Patients were considered treated as adherent to the ABC pathway if they were adherent to all 3 ABC pillars.