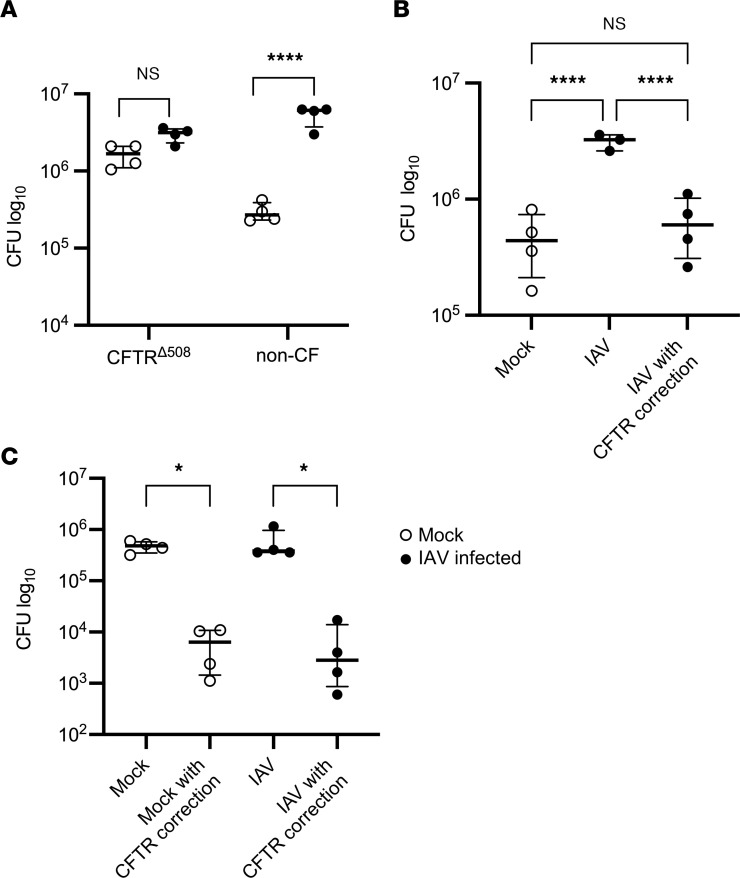
Figure 4. IAV increases Spn in the airway by inducing CFTR dysfunction.
(A) Non-CF and CFTRΔ508-HBECs were infected with 100,000 PFU of IAV for 72 hours, followed by infection with 1,000 CFU of Spn. Spn was quantified by vertical plating of apical washes after 6 hours of Spn infection (n = 4). (B) Non-CF HBECS were infected with IAV and basally treated with 10 μM lumacaftor and tezacaftor at the time of IAV infection, and then basally treated with 10 μM ivacaftor overnight before Spn infection. After 72 hours of IAV infection, HBECs were infected with Spn for 6 hours. Spn was quantified by vertical plating of apical washes (n = 3–4). (C) CFTRΔ508-HBECs were infected with 100,000 PFU of IAV and basally treated with 10 μM lumacaftor and tezacaftor at the time of IAV infection, and then basally treated with 10 μM ivacaftor overnight before Spn infection. After 72 hours of IAV infection, HBECs were infected with Spn for 6 hours. Spn was quantified by vertical plating of apical washes (n = 4). Panel A is representative of 2 independent experiments, panel B is representative of 3 independent experiments, and the experiment in panel C was conducted once due to limited availability of CFTRΔ508-HBECs. All panels were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s (A) or Tukey’s (B and C) multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001. Brackets indicate median and interquartile range. Open circles indicate mock IAV infection; closed circles indicate IAV infection.