Figure 5:
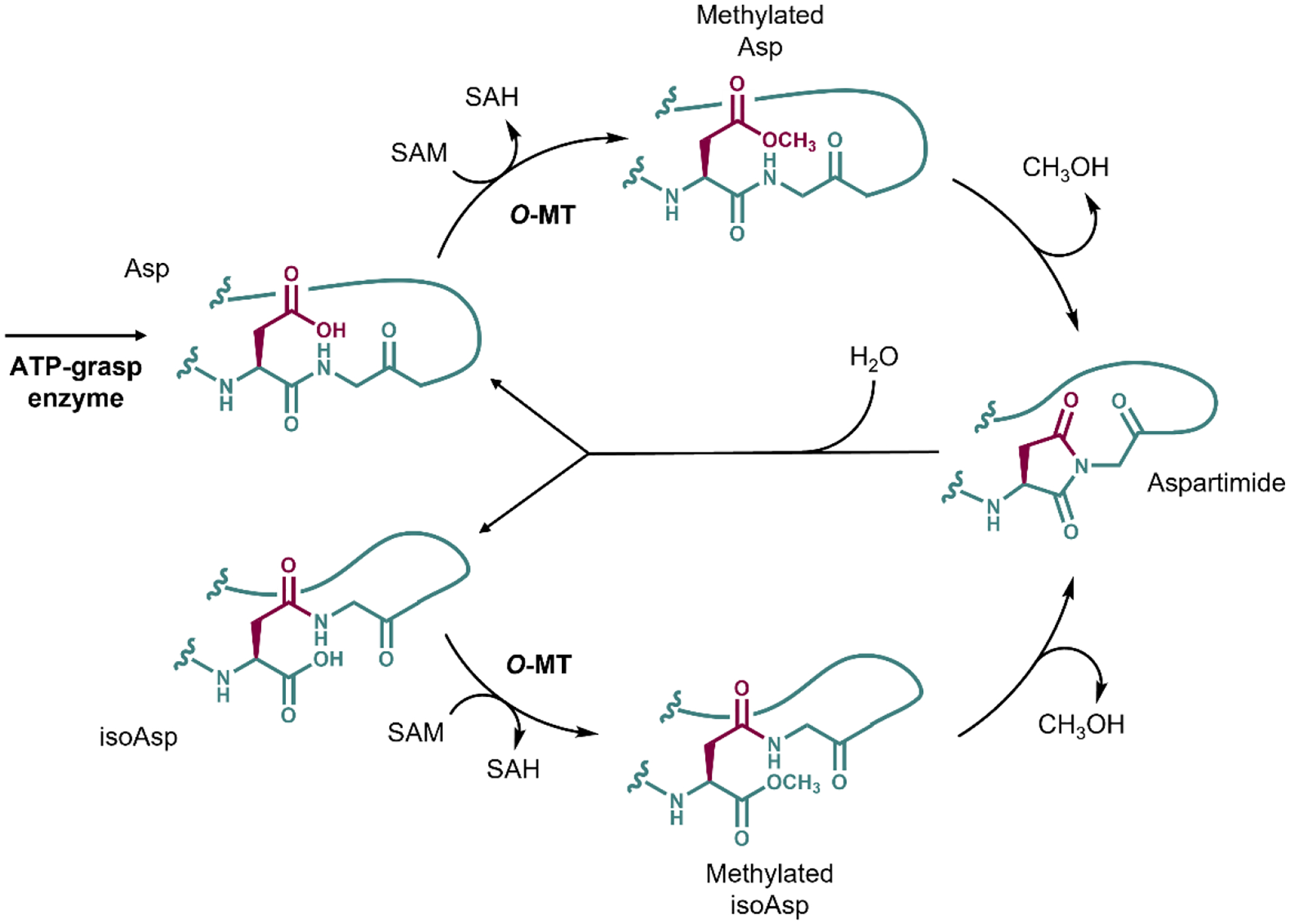
The aspartimidylation pathway of Group 13 graspetides catalyzed by O-MT. The original side chain of Asp is colored maroon, while the rest of the peptide is colored teal. The final product of the reaction catalyzed by ATP-grasp enzyme is the graspetide precursor with all ω-ester linkages with Asp in the aspartimidylation site. The O-MT methylates the Asp using SAM as a methyl group donor. The aspartimide forms spontaneously, resulting in CH3OH leaving the peptide. The aspartimide can be hydrolyzed at the side chain or the backbone, generating Asp (top) or isoAsp (bottom) at the aspartimidylation site. The O-MT recognizes both species, able to re-aspartimidylate the graspetide.
