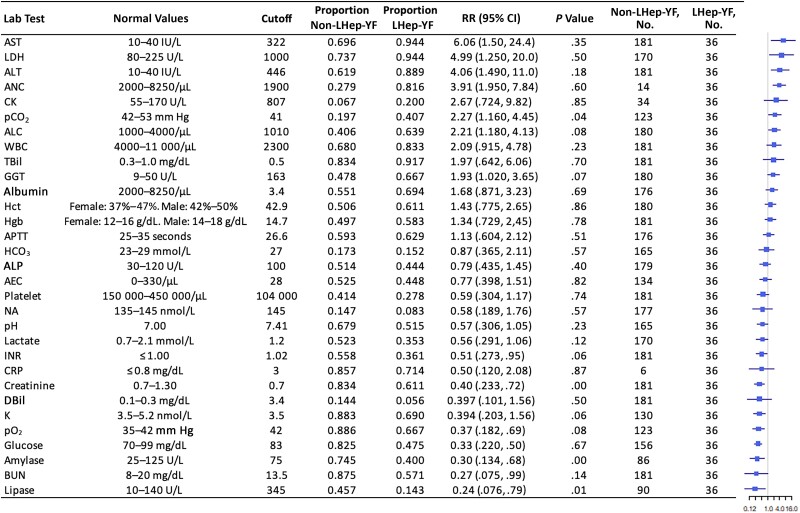
Figure 4.
Initial laboratory test values of Late-relapsing hepatitis after yellow fever (LHep-YF) and non-LHep-YF patients. From left to right, columns list the risk factor of interest (ranked by the magnitude of the relative risk [RR]), normal range values, the cutoff value selected for dichotomization, the proportion of non-LHep-YF cases above the cutoff, the proportion of LHep-YF cases above the cutoff, RR with 95% confidence interval, the P value comparing the 2 populations by Wilcoxon ranked-sign test, the number of patients analyzed in the non-LHep-YF group, and a forest plot illustrating the RR (node) and intervals (whiskers) relative to a risk of 1 (vertical line), where nodes to the right of the line indicate that a value above the cutoff is associated with an LHep-YF outcome. Normal values are presented according to the American Board of Internal Medicine laboratory test reference ranges (January 2022) [12]. Abbreviations: AEC, absolute eosinophil count; ALC, absolute lymphocyte count; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin clotting time; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; CI, confidence interval; CK, creatine kinase; CRP, C-reactive protein; DBil, direct bilirubin; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; HCO3, Bicarbonate; Hct, hematocrit; Hgb, hemoglobin; INR, international normalized ratio; K, potassium; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LHep-YF, Late-relapsing hepatitis after yellow fever; NA, sodium; pCO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide; pO2, partial pressure of oxygen; RR, relative risk; TBil, total bilirubin; WBC, white blood cell count.