Figure 5.
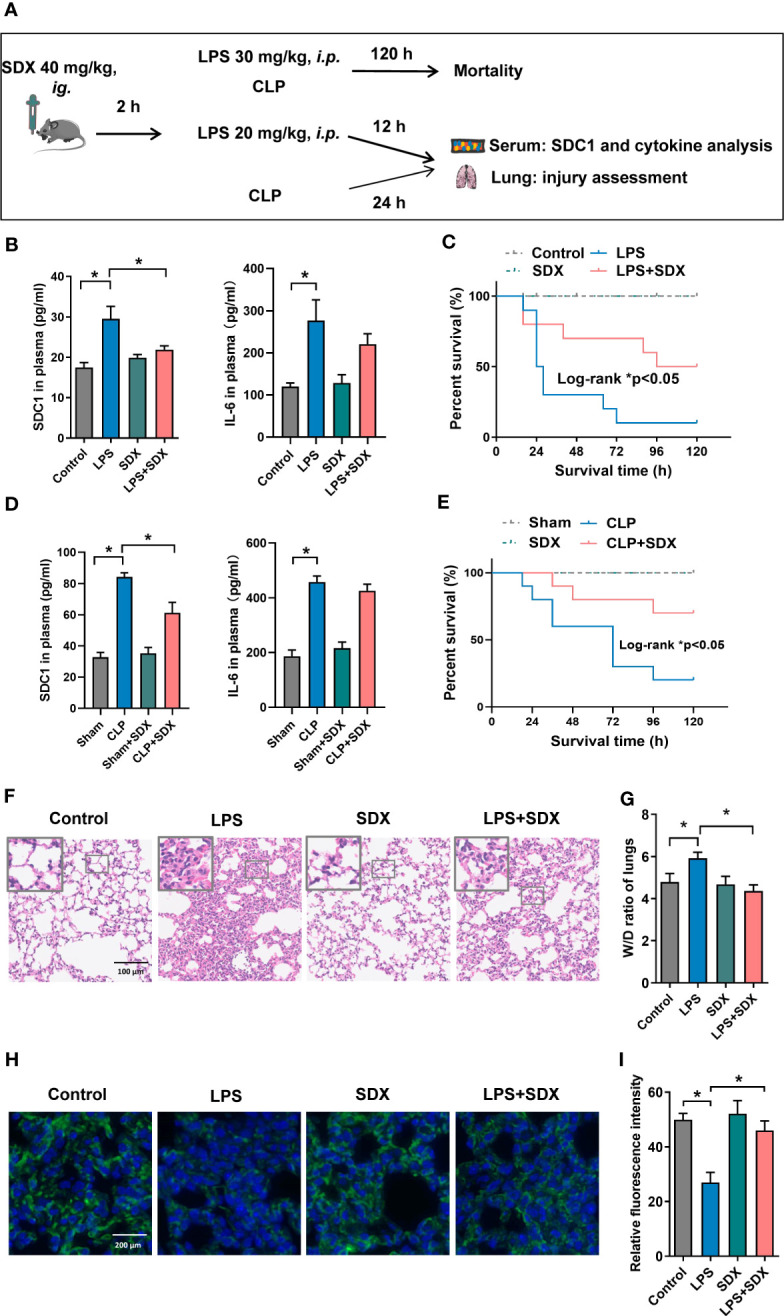
Inhibition of SDC1 shedding by Sulodexide improved lung injury and survival in septic mice. (A) Pattern diagram of the septic mouse model. Mice were pretreated with sulodexide (40 mg/kg) for 2 h before LPS injection or CLP procedure and those mice were observed for 12 h following LPS and 24 h following CLP before euthanasia. (B, D) ELISA to detect the plasma levels of SDC1 and IL-6 in the LPS (20 mg/kg)-challenged (B) and CLP-induced (D) septic model. (C, E) Survival curves after sulodexide administration to LPS (30 mg/kg)-challenged (C) and CLP-induced (E) mice, n=10/group/experiment. (F) Representative lung tissue sections stained with HE at ×100 (D) in LPS-induced sepsis model. (G) Lung tissue W/D weight ratio in LPS- induced sepsis model. (H) Representative immunofluorescence images of SDC1 in lungs, scale bar = 200 μm. (I) Densitometry of SDC1 immunofluorescence in lungs. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; *p < 0.05.
