Figure 3.
iNPC-GDNFs are neuroprotective in the SOD1 ALS rat
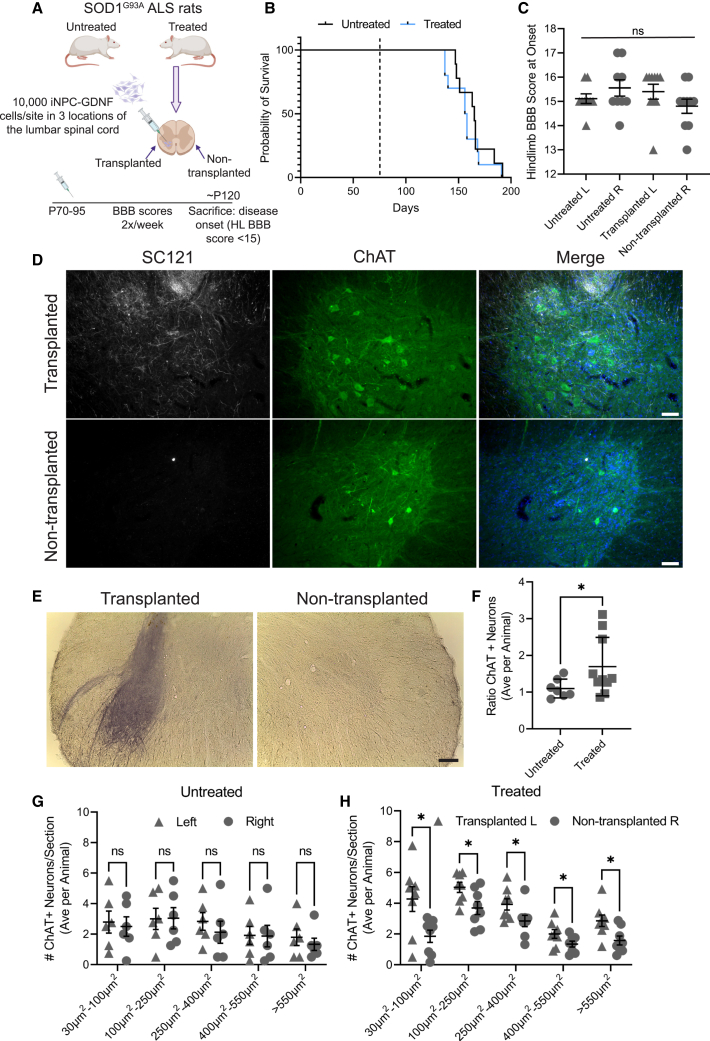
(A) Schematic of experiment. 10 male SOD1 rats at 70–95 days were unilaterally transplanted (left, L) with 10,000 iNPC-GDNFs in three sites 2 mm apart in the lumbar spinal cord and compared with 9 untreated animals.
(B) Kaplan-Meier shows probability of onset times of treated vs. untreated animals are not significantly different.
(C) Hindlimb BBB scores at disease onset are not significantly different.
(D) Immunohistochemistry shows SC121+ human grafts surrounding host ChAT+ motor neurons, with DAPI (blue).
(E) GDNF staining of transplanted compared with non-transplanted spinal cord.
(F) Ratio of ChAT+ motor neurons averaged per animal (n = 7 untreated and n = 10 treated animals).
(G and H) ChAT+ neuron size in (G) untreated animals (n = 6, average of four sections per animal) and (H) treated animals (n = 8, average of at least eight sections per animal); ∗p < 0.05 via unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (F) or multiple paired t tests corrected with the Holm-Šídák method (G and H); ns: not significant. Scale bars represent (D) 75 μm and (E) 250 μm.
See also Figure S3.