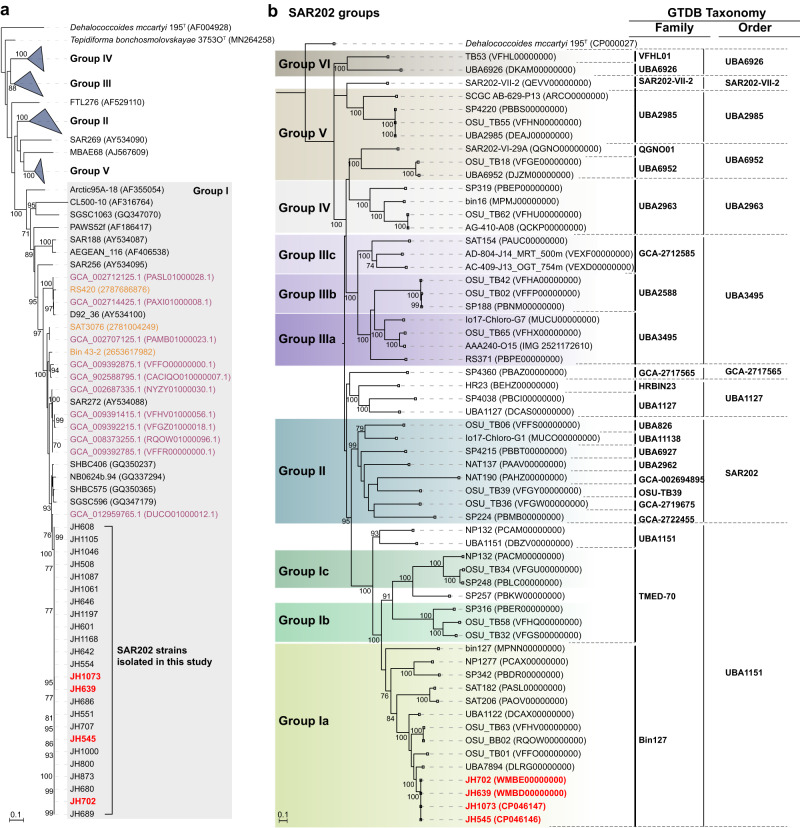
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic position of SAR202 strains isolated in this study.
a Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the relationship among the 24 SAR202 strains isolated in this study and closely related sequences retrieved from various databases, including GTDB (marked in purple), IMG (yellow), GenBank, and EzBioCloud. The four SAR202 strains selected for genome sequencing are marked in red. RAxML (v8.2.12) was used for tree building with GTRGAMMA model. Bootstrap supporting values (≥70%; from 100 resamplings) are indicated. Dehalococcoides mccarty was set as an outgroup. Bar, 0.1 substitutions per nucleotide position. b Phylogenomic tree of the SAR202 clade. The four genomes of SAR202 strains from this study (marked in red) and other MAGs and SAGs from previous studies were classified using GTDB-Tk. Species cluster-representative genomes of the GTDB taxa, into which the analyzed SAR202 genomes were classified, were included for tree building. Designation of the SAR202 subgroups following the classification scheme of a previous study12 is indicated on the left side of the tree with color shadings. On the right side of the tree, taxonomic assignment of the genomes at the family and order levels according to the GTDB (release 202) is shown. The tree building was performed using RAxML (v8.2.12), with PROTGAMMAAUTO option, based on a concatenated alignment of core genes obtained by UBCG pipeline. Bootstrap supporting values (100 iterations) are indicated on the nodes. Bar, 0.1 substitution per amino acid position.