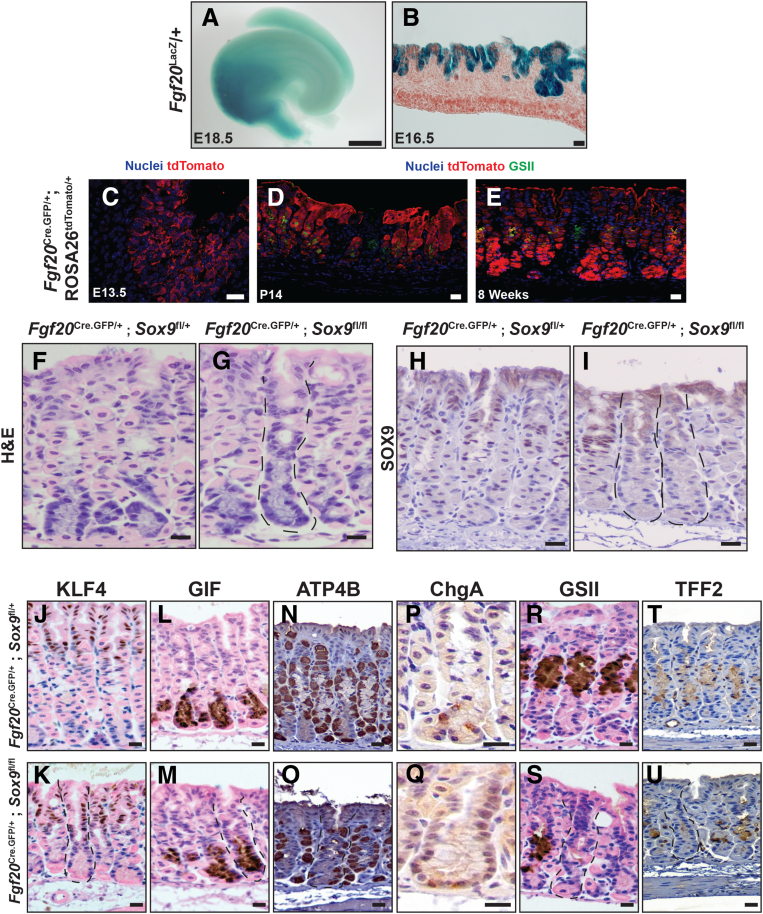
Figure 2.
Loss of Sox9 prevents mucous neck cell differentiation. (A) X-gal (5-Bromo-4-Chloro-3-Indolyl β-D-Galactopyranoside) staining of whole E18.5 stomach from a Fgf20LacZ/+ animal. X-gal staining was observed specifically within the glandular stomach domain of the stomach. (B) Section-based X-gal staining with nuclear fast red counterstain on E16.5 Fgf20LacZ/+ tissue. X-gal staining is specific to the gastric epithelium. (C) Immunofluorescence staining for nuclei (DRAQ5, blue) and tdTomato (mCherry antibody, red; ROSA26tdTomato). At E13.5 in Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; ROSA26tdTomato/+ animals, recombination of the ROSA26tdTomato was observed in a mosaic, salt-and-pepper pattern specifically within epithelial glandular stomach progenitors. (D and E) Immunofluorescence staining for nuclei (DRAQ5, blue), tdTomato (mCherry antibody, red; ROSA26tdTomatO), and GS-II lectin (mucous neck cell marker, green) at P14 and adult stages. (E) At P14, recombination of the ROSA26tdTomato allele in Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; ROSA26tdTomato/+ follows an all-or-nothing pattern: units have complete recombination throughout the unit from pit to base or no recombination at all. Identical recombination patterns were observed in adult units. (F) Representative histology of control 8-week-old corpus units, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (G) Representative Sox9-deficient unit (outlined) from Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; Sox9fl/fl mice. These units have alterations in cell morphology in the neck region, but the pit and base regions appear normal. Representative SOX9 immunohistochemistry from (H) control 8-week-old mice and (I) Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; Sox9fl/fl mice. Outlined units lack SOX9 expression. Representative staining on control animals and Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; Sox9fl/fl for (J and K) KLF4, (L and M) GIF, (N and O) ATP4B, (P and Q) chromogranin A, (R and S) GS-II lectin, and (T and U) TFF2. Control and Fgf20Cre.GFP/+; Sox9fl/fl mice have similar staining patterns for KLF4, GIF, and chromogranin A, indicating the pit, chief, and enteroendocrine lineages are not altered in the absence of Sox9. In contrast, there is a loss of GS-II lectin (S) and TFF2 (U) expression in Sox9-deficient tissue, indicating aberrant mucous neck cell differentiation. Scale bars: (A) 1 mm; (B–S), 20 μm.