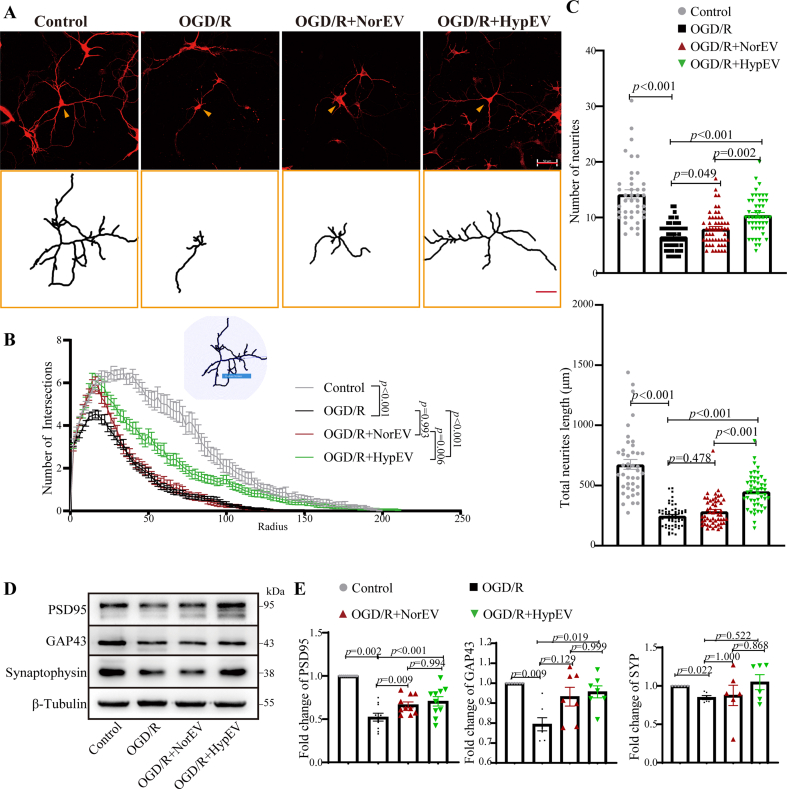
Fig. 4.
The effects of HypEV co-cultured with neurons in vitro. (A) After oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) injury for 3 h, the primary cortical neurons were incubated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), NorEVs, or HypEVs from primary cortical neurons for an additional 24 h in normal media. Microtubule-associated protein (MAP2) staining was used to characterize neuron morphology in vitro after neurons were incubated with PBS (OGD/reperfusion [R]), NorEV (OGD/R + NorEV), or HypEV (OGD/R + HypEV) (scale bar = 50 μm). The bottom yellow frame outlines single neurons (indicated by yellow arrows) using NeuronJ (scale bar = 50 μm). (B) An illustration showing the quantification of the dendritic complexity by Sholl analysis (upper part of the line chart). Intersections were used to quantify the MAP2-stained neural complexity (as shown in Fig. 4A). Numbers of intersections, total neurite length and neurite number of single neuron (C) are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 42–59 neurons per group from three experiments). Statistical significance was assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); differences between groups were considered significant if p < 0.05. The Control, OGD/R and OGD/R + HypEV groups were shared with Fig. 6C. (D) and (E) Representative Western blotting of postsynaptic density 95 (PSD95), growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43), and synaptophysin (a synaptic vesicle protein of the pre-synapse) in each group. Data are presented as means ± SEM, n = 6. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA; a value of p < 0.05 was considered significant.