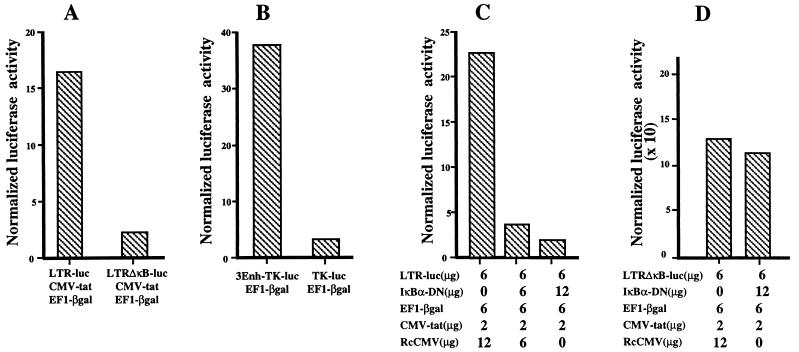
FIG. 4.
NF-κB activity is responsible for the high transcriptional activity of the LTR in thymocytes freshly isolated or cocultured with TEC. Freshly isolated thymocytes were cotransfected by electroporation with the following constructs: LTRluc, CMV-tat, and EF1-βgal (respectively used at 10, 5, and 10 μg per 107 cells) or LTR-ΔκB-luc, CMV-tat, and EF1-βgal (used at 10, 5, and 10 μg per 107 cells) (A); 3Enh-TK-luc and EF1-βgal (each used at 10μg per 107 cells) or TK-luc and EF1-βgal (used at 10 and 10 μg per 107 cells) (B); LTRluc, CMV-tat, and EF1-βgal (used at 6, 2, and 6 μg per 107 cells) and increasing amounts of IκBα-DN expression vector as indicated (C); and LTR-ΔκB-luc, CMV-tat, and EF1-βgal (used at 6, 2, and 6 μg per 107 cells) and 12 μg of IκBα-DN expression vector as indicated (D). Rc-CMV was added, as indicated, to normalize the amount of transfected DNA. Luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were determined 20 h after transfection in the thymocyte lysates. LTR activity was expressed as normalized luciferase activity. This experiment is representative of three independent experiments, each carried out on a different thymus.