Figure 4.
Construction and characterization of a humanized hRHOP23H/WT mouse model
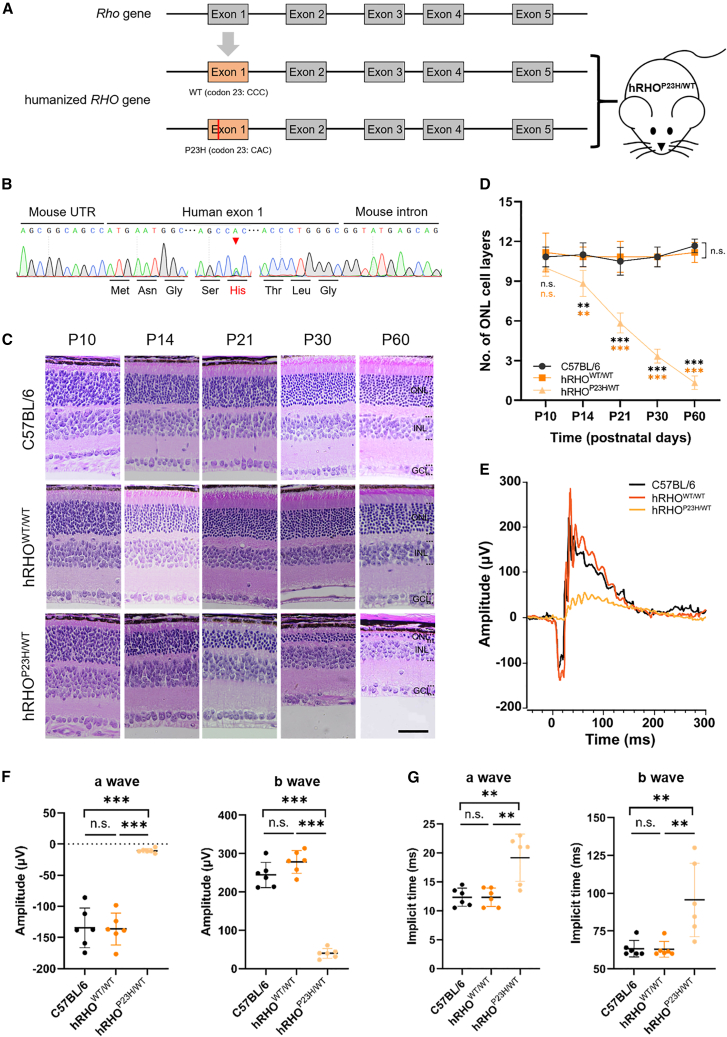
(A) Schematic diagram of strategy for construction of humanized RHO-WT and -P23H knockin mice. The exon 1 of mouse Rho gene (in gray) was replaced with corresponding normal (WT) or c.68C>A mutation (P23H) exon (in orange) of human RHO gene. (B) Genotyping validation of hRHOP23H/WT mouse by sequencing. Red arrow indicates the double peaks of C and A base. (C) Representative images of HE staining of C57BL/6, hRHOWT/WT, and hRHOP23H/WT retinas at age of postnatal 10, 14, 21, 30, and 60 days, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm. ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. (D) ONL cell layer numbers statistics of C57BL/6, hRHOWT/WT, and hRHOP23H/WT retinas at age of postnatal 10, 14, 21, 30, and 60 days, respectively. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., not significant; two-way ANOVA test. Three retinas for each group. (E) Representative ERG histograms of C57BL/6, hRHOWT/WT, and hRHOP23H/WT retinas at age of postnatal 30 days, respectively. (F) a- and b-wave amplitude statistics of C57BL/6, hRHOWT/WT, and hRHOP23H/WT retinas at age of postnatal 30 days, respectively. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., not significant; one-way ANOVA test. Six retinas for each group. (G) a- and b-wave implicit time statistics of C57BL/6, hRHOWT/WT, and hRHOP23H/WT retinas at age of postnatal 30 days, respectively. ∗∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant; one-way ANOVA test. Six retinas for each group.