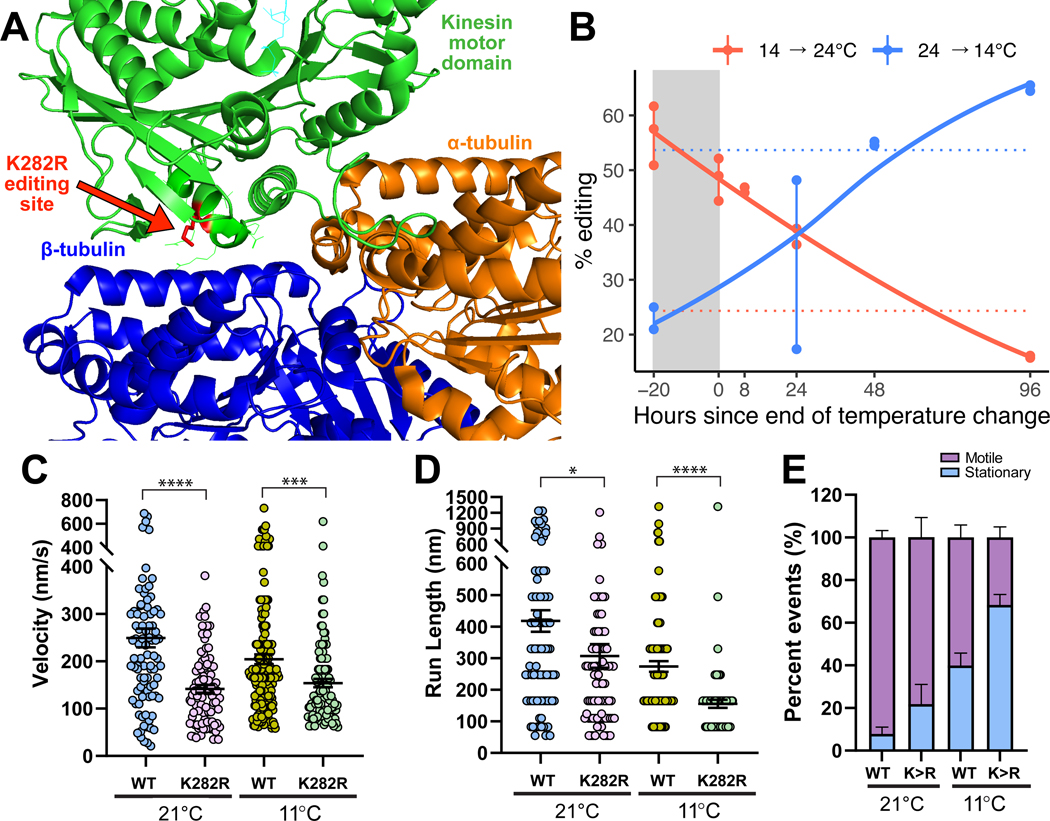
Figure 4: An editing site (K282R) on the motor domain of kinesin-1 is highly temperature-sensitive and induces strong changes in motility.
Panel A: Human monomeric kinesin (KIF5B) bound to tubulin (RCSB: 2P4N). Side chains are revealed for editing site and 10 conserved neighboring residues. Panel B: The K282R editing site is highly temperature-sensitive. Point data are shown from amplicon sequencing of a 4-day time-lapse experiment. Dotted horizontal lines represent editing levels during long-term temperature exposures at 13°C (blue) and 22°C (red). Panels C-E: Motility properties of individual wild-type (WT) and edited (K282R) octopus kinesin-1 along taxol-stabilized microtubules was visualized using single-molecule TIRF microscopy. From kymographs, the C) velocity, (D) run length, and (E) proportion of motile and stationary kinesins were determined. Motility properties were compared between wildtype (WT) and edited (K282R) kinesins at 21 and 11°C (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; and ****, p<0.0001). Panel E: The proportion of motile and stationary kinesins observed along microtubules were compared between WT and K282R and between temperatures. Error bars represent standard error. See also Figure S4.