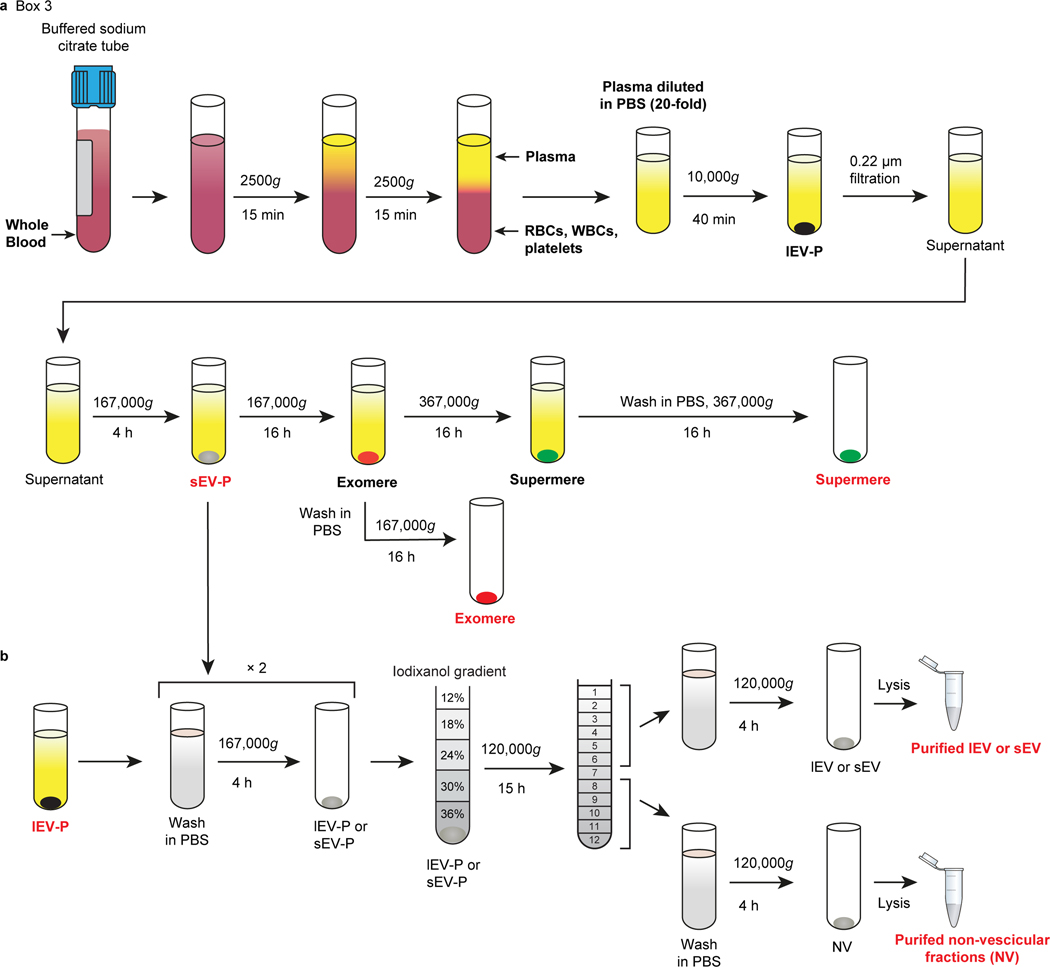
Fig. 3. Schematic of the isolation procedure for lEV, sEV, exomeres and supermeres from human plasma.
a, Schematic for isolation of different fractions from plasma. Plasma is generated by centrifugation of the blood at 2500g for 15 min twice at room temperature (RT). The resulting plasma samples are immediately diluted ∼1:10–20 in ice-cold PBS-H and centrifuged at 10,000g for 40 min to pellet lEV-Ps. The supernatant is filtered through a 0.22 μm pore PES filter and the resulting supernatants are subjected to sequential ultracentrifugation at 167,000g for 4 h, and 16 h, and then at 367,000g for 16 h to isolate sEV-Ps, exomeres and supermeres, respectively. b, Schematic of the generation of purified plasma lEVs, sEVs and NV fractions by high-resolution iodixanol density-gradient fractionation (12–36%). Crude pellets of lEV-Ps or sEV-Ps Crude pellets of lEV-Ps or sEV-Ps are processed as described in Fig. 2. The images are modified from Zhang et al.15 and Jeppesen et al.9. The research conducted as part of this protocol complies with all the relevant ethical regulations. The use of the human samples was approved by the Vanderbilt University Medical Center Institutional Review Board (IRB; IRB nos 161529 and 151721).