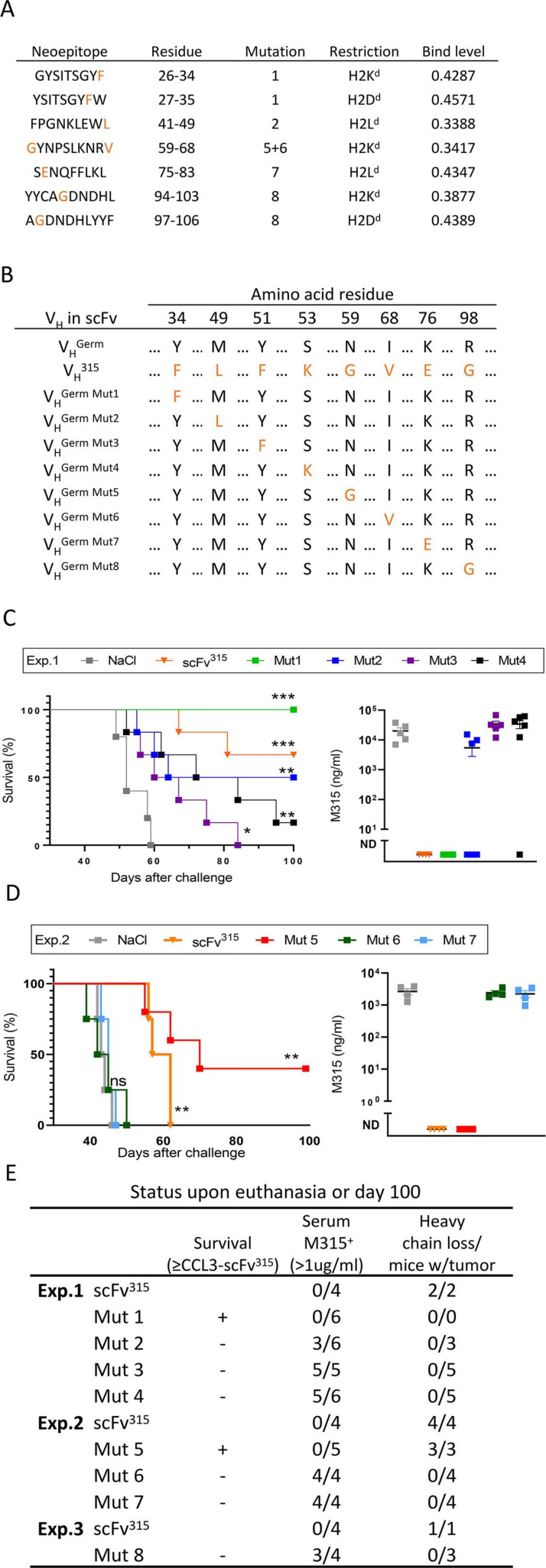
Figure 4.
Somatic mutations in VH 315 are essential for the ability of DC-targeted DNA vaccines to induce protection against MM cells. (A) Overview of neoepitopes predicted using NetMHCpan4.0. Strong binders containing a VH 315 mutation are shown. Mutations present in VH 315 are highlighted in orange. B) Overview of mutant VH used in scFv constructs used for immunization. Germline VH residues are shown in black, VH 315-specific residues in orange. All scFv constructs included VL 315. Below, the constructs are abbreviated as Mut1 etc. (C, D) BALB/c mice were immunized i.m./EP with 50 µg DNA or NaCl i.m. and challenged 14 days later intravenous with (2×105) MOPC315.BM.Luc.IgAλ2 (C) or MOPC315.BM.Luc (D), n=4–6 mice/group. Shown are survival curves (left) and M315 levels in sera at end point (right). (E) Summary of the effects of the different VH mutations in Exp 1 (figure 4C), Exp 2 (figure 4D) and Exp 3 (online supplemental figure 8) at end point (either day at paraplegia or day 100). Statistics: Mantel Cox log-rank test compared with NaCl group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. MM, multiple myeloma; ND, not detected; ns, not significant.