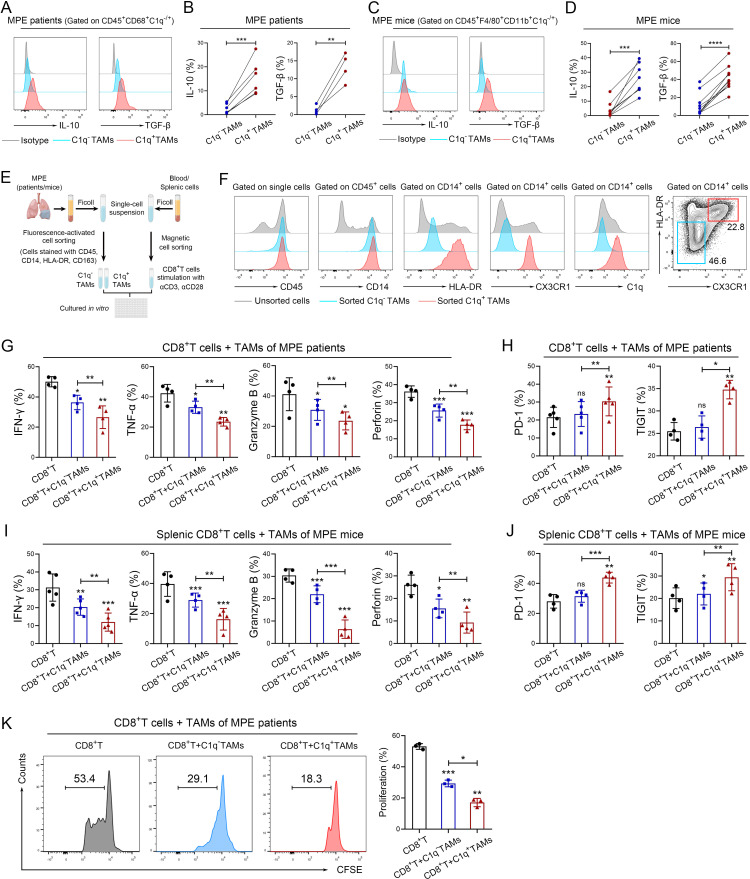
Figure 3.
C1q+ TAMs impair the antitumor responses of CD8+ T cells. (A–D) Tumor-infiltrating immune cells were isolated from human MPE (A–B) and mouse MPE (C–D); The expression of IL-10 and TGF-β in TAMs were analyzed using flow cytometry (n=4–8). (E) Schematic diagram of a co-culture system involving macrophages and CD8+ T cells (macrophages: CD8+ T cells=2:1) was drawn by FigDraw (www.figdraw.com; ID: IYYPP2af53). (F) The efficiency of fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) for C1q+ TAMs in human MPE was confirmed by the expression of C1q. (G and H) C1q+ and C1q− TAMs were isolated from human MPE by FACS, CD8+ T cells were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors by magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS). The tumor-killing activities (IFN-γ, TNF-α, granzyme B and perforin) and exhaustion‐related molecules (PD-1, TIGIT) of CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after co-culturing with TAMs for 72 hours (n=4–5). (I and J) C1q+ and C1q− TAMs were isolated from MPE mice by FACS, and CD8+ T cells were isolated from mouse spleen by MACS; tumor-killing activities (IFN-γ, TNF-α, granzyme B and perforin) and exhaustion‐related molecules (PD-1, TIGIT) of CD8+ T cells were determined by flow cytometry after co-cultured with TAMs for 72 hours (n=4–5). (K) C1q+ and C1q− TAMs were isolated from human MPE by FACS, CD8+ T cells were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors by MACS. CFSE assay was performed to detect the proliferation of CD8+T cells after co-cultured with TAMs (n=3). Data shown in (A–D), (F–K) are representative of at least three independent experiments (mean±SD). Statistical analysis was performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test (B, D, G–K). *P<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns: not statistically significant. C1q, component 1q; CFSE,carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; MPE, malignant pleural effusion; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TIGIT, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domains; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.