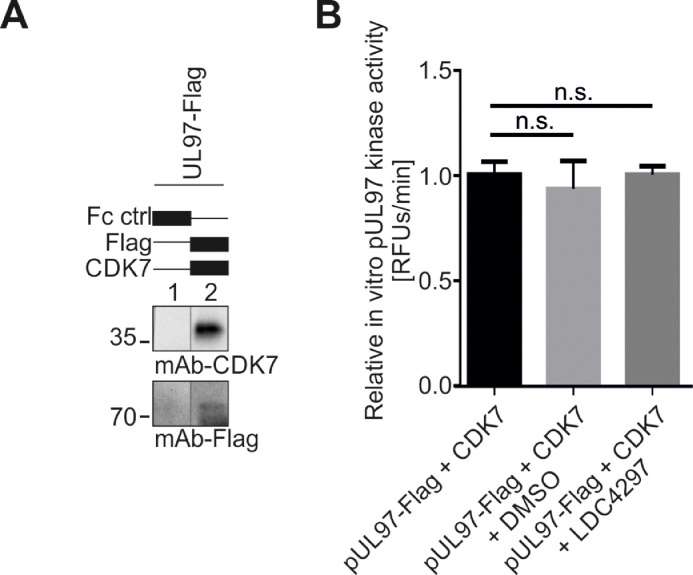
Fig. 6.
Human CDK7 does not increase pUL97 in vitro kinase activity. (A) 293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding pUL97-Flag. Cells were lysed 2 d post-transfection, and pUL97-Flag and CDK7 were immunoprecipitated using the indicated antibodies; a mouse Fc fragment served as a negative control. Dynabeads-bound proteins were eluted in 150 µl enzyme buffer. 25 µl of eluted Dynabeads were denatured in 25 µl 2x loading buffer and subjected to SDS-PAGE and Wb to confirm successful precipitation of pUL97-Flag and CDK7. (B) Samples derived from immunoprecipitation of CDK7 plus pUL97-Flag, as well as Fc control samples, were subjected to a qSox-IVKA (using the pUL97-specific sensor peptide AQT0258). Optionally, 0.01 µM of CDK7-specific inhibitor LDC4297 (corresponds to the mean antiviral EC50 value) or equal amounts of DMSO were added to the reactions. Background activity determined with the Fc control was subtracted from values of combined pUL97-Flag plus CDK7 kinase activity. Mean values ± SD derived from one representative experiment are given, as derived from measurements in triplicates. Statistical analysis was performed using an ordinary two-way ANOVA: n.s., not significant.