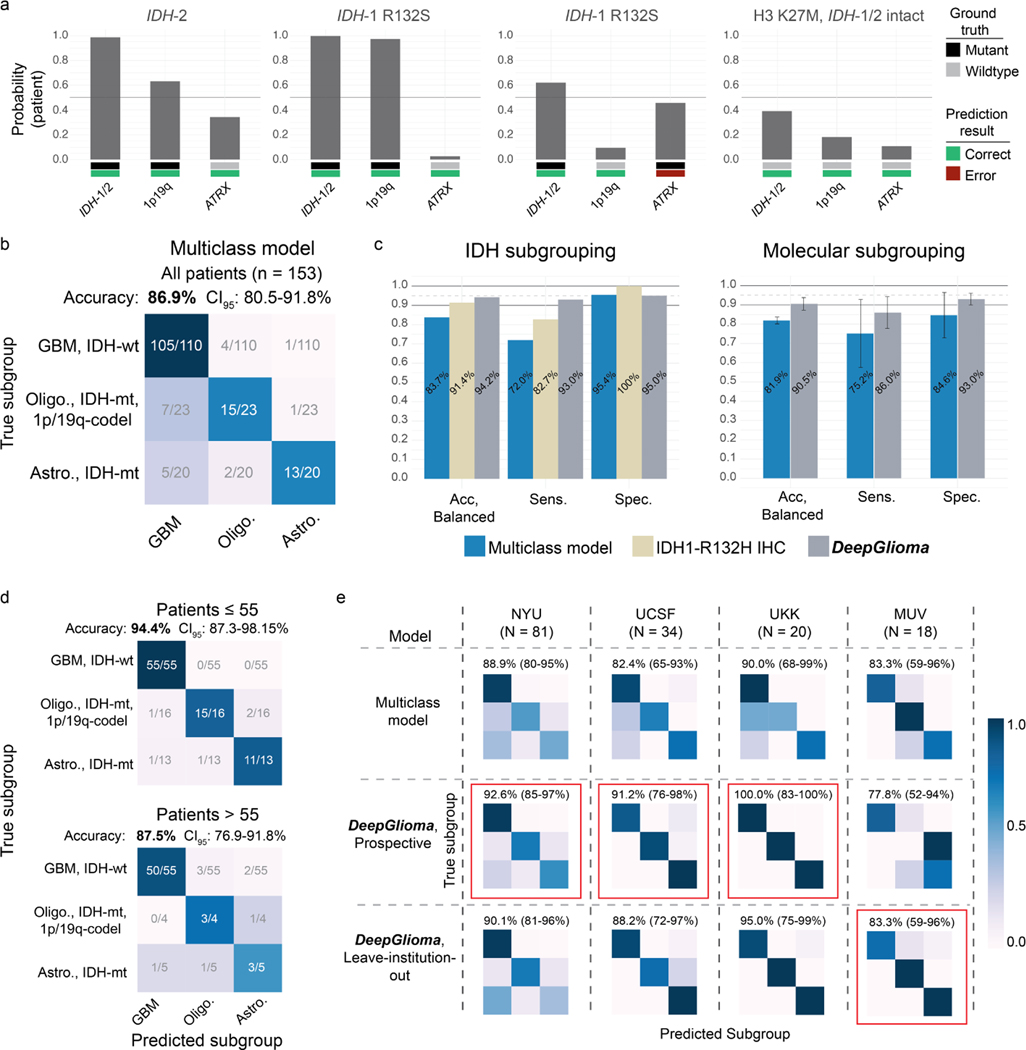
Extended Data Fig 8. Patient subgroup analysis of DeepGlioma performance.
a, Subset of patients from the prospective cohort with non-canonical IDH mutations and a diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27M mutation. DeepGlioma correctly classified all non-canonical IDH mutations, including IDH-2 mutation. Moreover, DeepGlioma generalized to a pediatric-type diffuse high-grade gliomas, including diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered, in a zero-shot fashion as these tumor were not included in the UM training set. This patient was included in our prospective cohort because the patient was a 34 year old adult at presentation. b, Confusion matrix of our benchmark multiclass model trained using categorical cross-entropy. DeepGlioma outperformed the multiclass model by +4.6% in overall diagnostic accuracy with a substantial improvement in differentiating molecular astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas. c, Direct comparison of subgrouping performance for our benchmark multiclass model, IDH1-R132H IHC, and DeepGlioma. Performance metrics values are displayed. Molecular subgrouping mean and standard deviations are plotted. d, DeepGlioma molecular subgroup classification performance on patients 55 years or younger versus patient older than 55 years. The overall DeepGlioma performance remained high in the ≤ 55 cohort, maintaining a high multiclass accuracy compared the entire cohort. DeepGlioma was trained to generalize to all adult patients. b, DeepGlioma molecular subgroup classification performance for each of the prospective testing medical centers is shown. Accuracy (95% confidence intervals) are shown above the confusion matrices. Overall performance was stable across the three largest contributors of prospective patients. Performance on the MUV dataset was comparatively lower than other centers; however, some improvement was observed during the LIOCV experiments. Red indicates the best performance.